Lithuanian corporate immunisation level is as high as 90% while others are below 30%

The share of immunised staff in different commercial companies may vary several times, the survey by Creditinfo Lithuania suggests. According to Statistics Lithuania (SL), the least immunised retailers (from 36.9 to 52%) work at markets and kiosks. The largest proportion of immunised staff after vaccination (up to 74.7%) has been reported in pharmacies, optics and supermarkets. Among all the sectors, the least active are construction and transport companies, but this indicator may well be explained by a large share of foreign nationals on their staff list.
According to SL data, in terms of the share of immunised staff in the commercial sector, companies selling bread, buns and confectionaries in specialty bakery shops take the last place, with slightly over one third (36.9%) of immunised staff. In other commercial segments, the percentage of fully immunised staff is within the range of 52–64%, with 60–87.2% of staff having received at least one vaccination doze.
Jekaterina Rojaka, Head of Business Development and Strategy at Creditinfo Lithuania, says that after the Statistics Lithuania launched publication of immunisation indicators on a company level, Creditinfo followed suit and started reflecting them in its information systems, while a growing number of users look for information on immunisation of potential business partners.
More staff got infected and recovered from the virus where the vaccination pace is slow
It appears from the publicly available data that in companies with staff delaying vaccination the proportion of staff infected or having recovered from the virus is higher. Obviously, the analysis of recovery indicators among staff suggests that many of these people (up to 12%) are among market and kiosk retailers. Within the category, the sub-category of textile, clothing and footwear retailers stands out where the full immunity (two vaccine dozes) within this group has been acquired by 52% of staff, another 12% of staff became immune after getting infected and recovering from the virus, bringing the overall immunisation level to 64%.
In comparison to workers in supermarkets, pharmacies and optics with 75% of fully vaccinated staff, the immunity after getting infected with the virus was reported from 1 to 5% of the labour force.
The largest number of immunised staff work for the financial services sector, the smallest number – in transport companies
The analysis of companies from other economic sectors suggests that among companies with 70–100% of immunisation level, those engaged in financial activities and services take the lead with 87.1% of immunised staff. Companies at the bottom of this group are from construction (38.7%) and transport sectors (30.3%). According to J. Rojaka, a low level of vaccination there may be explained by a relatively high number of foreign staff working in these sectors, leaving their immunisation indicators outside the scope of the national statistics.
Compared to other economic sectors, extractive industry and agricultural companies are moving at the slowest pace towards the set immunisation target of 70–100%, accounting for 46.6 and 47.8% of immunised staff, respectively.
In restaurants and hotels, which had been very actively promoting vaccination among their staff, at the end of August the immunisation indicator approached to 71.5 and 71.6%, respectively. J. Rojaka notes that these two sectors have achieved the major quality progress in terms of staff vaccination pace, reporting an increase of 45 percentage points in the number of staff vaccinated in August.
For more information:
Jekaterina Rojaka,
Head of Business Development and Strategy, Creditinfo Lithuania
Email: jekaterina.rojaka@creditinfo.lt;
Tel: +370 612 73515
Analysis of the Lithuanian construction sector

Financial and performance indicators in the construction sector reveal positive rather than negative trends. The boom in real estate emerging in the time of the pandemic has remarkably boosted the sectoral activity (during the first 6 months of this year alone the volume of constructions works grew by almost one fifth) and positively reflected in performance indicators of most of the companies. Sectoral earnings have been rapidly growing both on the domestic and foreign markets. After discounting the impact of seasonality and working days abroad, the volume of construction works is an increase of 21.5% year-on-year. The number of construction companies have been mushrooming, accounting for an increase by a third during the second quarter of this year compared to the previous year.
Financial statements filed by construction companies show that the number of construction companies in Lithuania in 2021 has grown by additional 531 from 15,784 to 16,316 (an increase of 3.4%) year-on-year. A very similar pace of growth (4.1%) was observed in the average corporate earnings (from EUR 809,994 to EUR 842,872). In terms of the staffing level, though, it has decreased slightly from 102,072 to 101,833. Despite a favorable situation, managers of construction companies are very cautious about the growth in the number of staff due to higher labour and other construction costs. Due to a more pessimistic mood in the sector, during summer this indicator started to decrease.
Another important positive factor is the decreasing number of debts and their aggregate values. For instance, during pre-pandemic August 2019 the number of corporate debts in construction industry stood at 12,336, with their aggregate value of EUR 128.7 mln. At the same period in 2020 the number of corporate debts stood at 11,539 compared against a reduced value of debt of EUR 94.3 mln. Although at the end of last August the number of corporate debts in the construction industry grew once again to 12,055, the aggregate debt value accounts for EUR 96.6 mln.
Some positive trends may be seen in the solvency of the construction industry. For instance, a year ago 23% of companies in this sector belonged to the high or highest group of bankruptcy risk, whereas this year the number of such companies dropped to 20%. In terms of delayed payments, some improvement may be observed too: last year the number of companies within the group of high and highest risk of delayed payments accounted for 47%, compared against 37% this year.
A number of construction companies going bankrupt has been decreasing steadily. In 2017-2020 the number of bankruptcies dropped from 366 to 163, whereas the updated statistics for this year give a solid ground to expect a further similar decrease in the number of reported bankruptcies.
Despite the reported drop in earnings in 2020 from 10% to 4% in comparison to 2019, other performance indicators in the construction industry have improved. For instance, the corporate sales median increased by 16% (from EUR 143,155 to EUR 166,133), the quick ratio has grown from 1.86 to 1.95, while the profit margin before tax increased from 1.25 to 1.35. The equity ratio has improved from 43.83 to 46.23, the accounts payable turnover decreased from 134 days to 128 days, whereas the accounts receivable turnover shortened from 57 to 51 day. EBITDA grew from 9.1 to 12.3%.
Jekaterina Rojaka,
Head of Business Development and Strategy, Creditinfo Lithuania
Creditinfo Lithuania included immunization levels into its list of corporate indicators

After the Department of Statistics launched publication of immunization levels in specific companies, credit office Creditinfo Lithuania immediately included this indicator into its corporate reports. From now on, clients ordering detailed information about a selected company will be able to see the proportion of immunized staff.
“The inclusion of immunization indicator into corporate reports will facilitate a better risk analysis of potential disruptions of activities due to staff illnesses which will help a business partner, or a client make further business decisions”, Aurimas Kačinskas, CEO of Creditinfo Lithuania said.
The first ever publication of immunization levels has demonstrated that, e.g., the largest share of immunized staff (80%) work for the IT sector, and the least immunized staff (as little as 27%) work for transportation companies. In comparison, as many as 80% of Creditinfo Lithuania staff have already been vaccinated.
Moreover, the official information published by the Department of Statistics will soon enable comparison of the share of immunized staff in one enterprise with counterpart organizations in the same business sector. To this end, an additional indicator is published as well – the so-called percentile. For instance, if an enterprise’s percentile is 100, it means that it is among one percent of companies with the highest immunization level. The lower the percentile, the fewer employees have immunity, i.e., have been vaccinated with at least one doze or have recovered from the coronavirus.
According to the Department of Statistics, for the purpose of confidentiality the percentage of immunization is indicated only for those workplaces with over 10 members of staff.
“We believe that monitoring these indicators contributes to the national fight against the Covid-19 pandemic, encouraging companies to take a more proactive approach with regard to staff vaccination”, A. Kačinskas said adding that “we always try to include new indicators into our reports in a timely manner so that our clients could benefit from exhaustive information about other companies”.
As of last May, Creditinfo Lithuania included into the list of monitored indicators information about average gender pay, and soon is planning to introduce yet another one – the sustainability indicator.
TOP 1000: Lithuanian leaders demonstrated outstanding resilience

In Lithuania, Creditinfo actively cooperates with business media, providing diverse analytical information in the form of various sectoral reviews and highlighting trends in the key business performance indicators. Every year the main business media channel, the Verslo žinios (Business News), publishes a list of TOP 1,000 largest Lithuanian companies reflecting on the changes that took place over the last year.
In July, the Verslo žinios published its latest update of TOP 1,000 list of business companies compiled based on Creditinfo’s data and corporate financial statements filed in 2020. Luckily, a positive trend can be seen: as many as 59 percent of companies saw their income grow over the last year, which was stimulated also by decision of the global leaders aiming at economic recovery.
At the courtesy of the Verslo žinios editorial staff we are publishing a part of the exhaustive publication; the link to the original article is provided at the end of the text.
—————————————————————————————————————————————————
Published on 16 July 2021.
- The Verslo žinios presents the latest update of TOP 1,000 list of Lithuanian companies.
- Major businesses have successfully adjusted to the new reality.
- Business leaders generated 24.7% more pre-tax income in 2020 than before the pandemic.
- According to Creditinfo’s data, one third of TOP 1,000 companies reduced the likelihood of delayed payments.
- Biotechnological company UAB “Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics” skyrocketed to the third position on the list.
Contrary to the gloomy pandemic predictions, the pre-tax income of the 1,000 largest Lithuanian companies in 2020 grew by a quarter. Although some of the major corporations were hit really hard by COVID-19, a substantial proportion of them rose up to the challenge transforming themselves and reporting unexpected returns.
These trends are reflected in the TOP 1,000 list of the largest Lithuanian companies drawn jointly by the Verslo žinios and Creditinfo based on income data for 2020. The list includes companies which filed their financial statements in time, i.e., by 31 May, with the Centre of Registers (CR).
Income plummeted against growing profit
Traditionally, the TOP 1,000 list is dominated by companies from three economic sectors, such as: wholesale and retail (381 company), manufacturing (263 companies), transportation and storage (136 companies). All these taken together account for more than three fourths of all the companies on the list.
Almost 500 of businesses are located in Vilnius county, another third operates in Kaunas and Klaipėda counties (223 and 107 companies, respectively). The list includes 76 companies with fewer than 10 employees.
Last year 1,000 of the largest Lithuanian companies generated EUR 51.3 bln. income, i.e., 1.3% less than in 2019. However, in aggregate, these companies earned EUR 3.3 bln. of pre-tax profit, which is an increase of 24.7% from 2019.
Profit of major companies grew the fastest
The growth of TOP 1,000 companies was far more robust than that of the reminder businesses. According to preliminary estimates of the Department of Statistics, in 2020 in Lithuania non-financial companies generated EUR 96.3 bln. income and EUR 6.7 bln. pre-tax profit: in comparison to 2019, the income shrank by 0.4%, while pre-tax profit grew by 3.9%.
Last year 10 companies passed a symbolic threshold of 0.5 bln. of sales income, five of which are retail or wholesale companies. Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, UAB skyrocketed to the third place on the list, reporting EUR 1.26 bln. in turnover.
“Despite the prevailing trend of moderately shrinking income amongst the largest 1,000 Lithuanian companies compared against 2019, and a decreasing number of staff, companies generated almost 25% higher profit before tax. An obvious leader in this category is the biotechnological company Thermo Fisher Scientific Baltics, UAB – a manufacturer of COVID-19 reagents and vaccine components. Its pre-tax profit reached EUR 472.6 mln., thus securing the company the first place among the leading companies in terms of this indicator”, said Jekaterina Rojaka, head of business development and strategy at Creditinfo.
According to Indrė Genytė-Pikčienė, chief economist at INVL Asset Management, UAB, a more rapid profit growth among the top 1,000 companies demonstrates the success of major companies in making the best out of the pandemic situation.
Usually, due to the advantage of scale, large companies have more leverage and freedom of manoeuvre than the smaller ones in the face of unexpected circumstances, when they have to negotiate with creditors, suppliers, and other partners”, she explained.
The original publication may be accessed here: https://vz.lt/finansai-apskaita/2021/07/16/top-1000-lietuvos-verslo-lyderiai-parode-neitiketina-atsparuma
Authors:
Eglė Markevičienė
Jovita Budreikienė
Increased use of credit bureau data in Lithuania

The use of credit bureau data is growing along with economic activity, although businesses tend to undertake additional precautions
The INTRUM EPR 2021 survey published in June reported on the growing demand for pre-payments against a decreasing trend of conventional risk management measures, such as credit history screening, insurance and factoring.
The current situation in the business sector could benefit from some clarifications and comments. In turbulent and uncertain times – and lockdown could rightly be said as being one of these – entrepreneurs tend to undertake additional safeguards, e.g. pre-payments. However, any quantitative easing measures, such as material support offered in the form of soft credits or subsidies, enabled many businesses to maintain their liquidity at least for some time. This is why the corporate performance results were not as devastating as they were during the Great Recession, when manufacturers importing commodities were forced to allocate all of their funds for pre-payments to their suppliers.
Meanwhile, the statistics demonstrates some late payments to the partners in 2021 in the sector of hospitality industry (by 9 days, from 41 to 50), in transport (from 56 to 62 days), in services (from 38 to 41 days), in processing industry (from 38 to 40 days). In contrast, in the financial operations sector, the payment terms have become shorter.
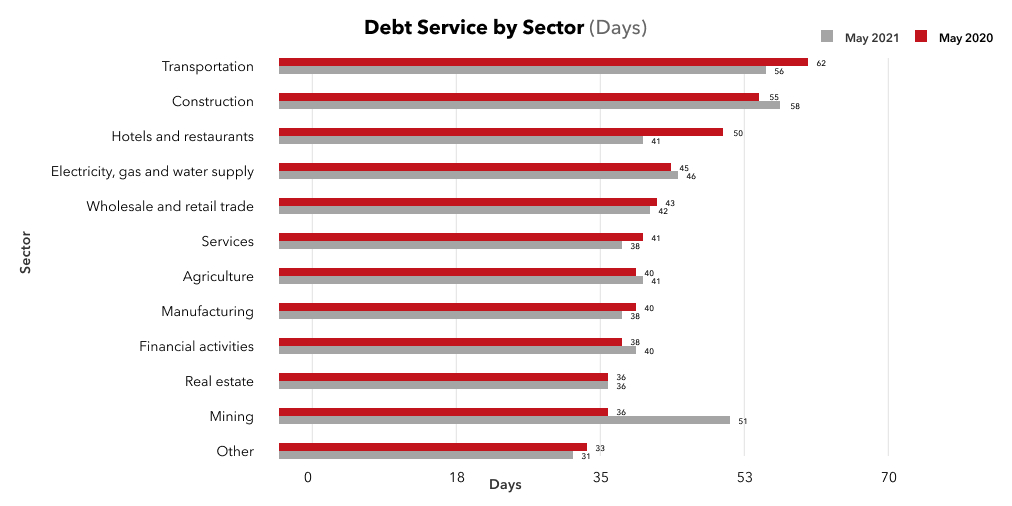
Quite reasonably, one may wonder what are the reasons behind shorter payment terms – can these be explained by precautions taken by the suppliers or by an improving economic situation?
I would like to draw the attention to the fact that in the times of the pandemic shareholders would recommend public sector representatives tightening payment gaps to enable the business sector to improve liquidity in the private sector. In the private sector the medium-term payment gaps were affected by a more resilient economic structure, as businesses suffering from liquidity shortage made only a fraction of all businesses.
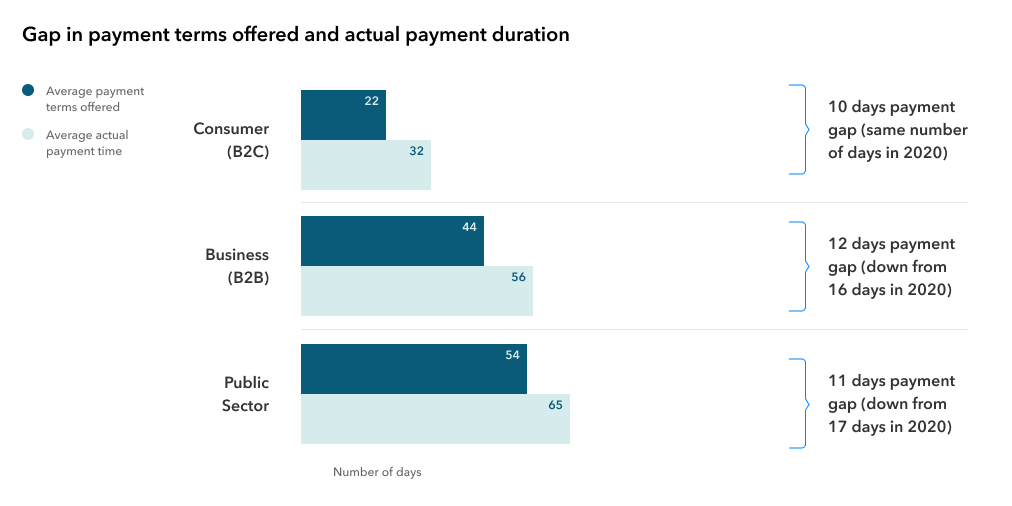
Moreover, account needs to be taken of the fact that as many as 60 percent of companies responding to the INTRUM survey in Lithuania admitted anticipating recession in contrast to economic forecasts showing a clear recovery.
Lithuanian business market is rather optimistic: the economic evaluation index in Lithuania has already reached its pre-pandemic level (116 vs. 110), this indicator was higher only in 2007 on the eve of the Great Recession. In addition, all sectors last May demonstrated a growing confidence index. Commercial confidence index grew by 9 percentage points, while in the service, industry, and construction sectors it grew by 7, 4, and 1 percentage points, respectively. Only the consumer confidence index dropped by 3 percentage points.
In parallel, a rapid growth in the real estate prices and demand is being reported along with the signs of growth in the prices of commodities and inflation. All these factors may signal the approaching peak in an economic cycle, which explains the lingering anxiety about a possible recession due to the phasing-out of economic stimulus measures.
One of the most popular support measures – tax deferrals – are drawing to an end: default interests and tax recovery procedures will not be calculated until 31 August 2021 and for two subsequent months; one may expect to see a more realistic state of business health towards the end of the year.
Nevertheless, the following conclusion has to be drawn as a comment on the use of credit office information systems by the organizations: the number of inquiries recently has been changing along with the economic activity – within the first 5 months the number of inquiries increased by 12 percent compared to 2020 year-on-year, and by as many as 25 percent compared to 2019 year-on-year.
Jekaterina Rojaka,
Head of Business Development and Strategy,
Creditinfo Lithuania.
Creditinfo Lithuania study: Men earn more than Women

In Lithuania men earn more than women in 72 economic sectors, while women do so in 9 sectors. Human resource specialists recommend inquiring more boldly about corporate career and pay policies.
The study conducted by Creditinfo Lithuania suggests that out of 81 sectors into which economic activities of Lithuania-based companies are broken down, in 72 of them men earn more than women on average. Pay for men usually exceeds pay for women by roughly 30-50 percent, while the largest positive gender gap of 19.2 percent in favor of women has been recorded in education. In the reminder eight sectors women usually earn 8.5 percent more compared to men on average. The most striking gender pay gap favoring men is reported in 30 economic sectors where the highest monthly pay may range from EUR 1,464 to 2,671. Human resource specialists recommend staff inquiring about corporate pay and career policies.
As of May, when Sodra started publishing gender pay gap data, the credit bureau Creditinfo Lithuania has analyzed pay received in various economic sectors. The study suggests that in an absolute majority of activities, especially those with the highest pay, men usually earn more than women on average: in telecommunications (50.1 percent), in medicinal products and pharmaceutical services (47.8 percent), in veterinary activities (45.1 percent), in insurance and reinsurance (41.9 percent), in financial services (43.3 percent), in cinema and TV programme production (40,4 percent), in manufacturing of power generation equipment (38 percent), operation of headquarters and consultation activities (35.6 percent), in information services (37 percent), in production of computer, electronic and optical devices (34.8 percent), in research and experimental activities (34.8 percent), in programme production and broadcasting (34 percent).
Sectors which particularly stand out are air transport, gambling, and gaming industry, where men earn 95.1 to 127.6 percent more than women on average.
There are several sectors where women are usually higher earners, such as: education (19.2 percent), land transport and transportation by pipelines (10.7 percent), social work (11.6 percent), in-house social care activities (8.3 percent), furniture production (7.2 percent), postal and courier services (6.2 percent), manufacturing of tobacco products (5.8 percent), and manufacturing of metal products (5.1 percent).
Publication of gender pay gap will boost corporate sustainability
According to Jekaterina Rojaka, the head of corporate strategy and development at credit bureau Creditinfo Lithuania, while analyzing the corporate operations other factors, in additional to the financial indicators, such as earnings and profit, are becoming increasingly more relevant – these factors determining the overall corporate reputation include operational transparency, corporate values and internal culture, staff and social responsibility policies.
“Sustainability is starting to play a more important role on the corporate creditworthiness and reliability, as it entails transparency in corporate policy on staff relationship, corporate policy on partners and communities, and contribution to solutions of issues important for the society”, J. Rojaka says. Statistics on average pay by men and women supplements information about the prevailing motivational instruments used by the company and career opportunities.”
According to J. Rojaka, gender pay gap is a particularly sensitive issue also because on the Lithuanian labour market men and women enjoy an equal employment rate. The Eurostat data suggests that in the age group of 20-64 in Lithuania the gender employment rate gap (with 79 percent of men and 77.4 percent of women having employment) is the lowest in the whole of the European Union, accounting for a mere 1.6 percent in Lithuania.
According to the data of the Department of Statistics of Lithuania, in 2020 in Lithuania there were 1.358 mln. people having employment – 679.9 thousand and 678.2 thousand of men and women, respectively. The employment rates of men and women in different economic sectors varies. For instance, there are many more men than women engaged in agriculture (2.06 times more or 52.2 thousand versus 25.1 thousand, respectively), in power and gas supply (4.3 times more, or 7.7 thousand and 1.8 thousand, respectively), in water supply and wastewater treatment (2.5 times more, or 13.1 thousand and 5.2 thousand, respectively), in construction (10.7 times more, or 91.2 thousand and 8.5 thousand, respectively), in real estate operations (1.6 times more, or 7.7 thousand and 4.8 thousand, respectively).
There are sectors, though, where women’s employment rate is several times higher than that of men’s, these sectors are: health care and social work (6.1 times higher, or 13.6 thousand and 83.1 thousand, respectively), education (3.9 times higher, or 27.7 thousand and 106.9 thousand, respectively), accommodation and catering (2.4 times higher, or 9.9 thousand of men compared to 23.7 thousand of women).
Among the sectors with a similar level of employment rate among both genders the average salaries paid to men remain higher than salaries of women. These sectors include wholesale and retail (104.1 thousand of men and 114.8 thousand of women), information and communication (23.6 thousand and 15.6 thousand), financial and insurance activities (9.9 thousand and 16 thousand), administration (30.8 thousand and 26.2 thousand), public administration and defense (43.2 thousand and 43.2 thousand), creative and leisure activities (10.1 thousand and 16.6 thousand).
Meanwhile, the representative of Creditinfo notes that while analyzing average salaries paid in any individual company account shall be taken of the gender balance, the positions held by men and women, as well as the competences and experience needed in the given position. Moreover, she notes that, for instance, in air transport pilots are usually men, while women mainly work as flight attendants, which explains a huge gender pay gap in the air transport sector.
Human resource specialists recommend analyzing data carefully and discuss about career and pay more boldly
Šarūnas Dyburis, the Managing Partner at AIMS International Lithuania, notes on a shrinking gender pay gap among staff with the same level of competences and experience.
“Overall, within the European Union Lithuania is somewhere in the middle in terms of gender pay gap – an average pay for men is 13.3 percent higher than that for women, compared against an EU average of 14.1 percent”, Š. Dyburis said. Our country stands out in that the gender pay gap has dropped to the minimum among men and women with the same level of experience and competences. However, due to objective reasons, such as career breaks due to maternity leave, women reach the highest pay levels slightly later than men, which also affects the average salaries”.
The head of AIMS International Lithuania notes on an increasing popularity of corporate motivational and pay policies in Lithuania offering clearer career possibilities, encouraging the pursuit of higher performance indicators, and strengthening of cooperation spirit within organizations.
“We would like to encourage women plan their career path more boldly, be more proactive in seeking new career opportunities, and negotiating for higher pay more ambitiously. All candidates without exception should openly inquire about corporate career policies and learn about staff achievement appraisal and motivational systems”, recommended Š. Dyburis.
For more information see:
- https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Gender_statistics#Labour_market
- https://osp.stat.gov.lt/lt/statistiniu-rodikliu-analize?hash=f3f0ba78-6fb2-433f-ad92-ef032be74a9e
For more information contact:
Jekaterina Rojaka, Head of business development and strategy at Creditinfo Lithuania (jekaterina.rojaka@creditinfo.lt; +370 612 73515)
Šarūnas Dyburis, the Managing Partner at AIMS International Lithuania (sarunas.dyburis@aims.lt; +370 616 72727)
The ‘Cornwall Consensus’ – A Credit Bureau Perspective

From a credit bureau perspective, a close partnership between government and business has always been essential to ensure the economic goals of a country are achieved. It was therefore interesting to see this relationship being promoted as part of the ‘Cornwall Consensus’ last week at G7.
Gillian Tett of the Financial Times was discussing this concept in a recent article which considered the ‘profound, reset under way of the relationship between business and government.’ Tett describes the change by which ‘companies were regarded as independent actors competing with one another, without state involvement,’ to a relationship which would result in more of a ‘“partnership” between government and business.’
From a credit bureau perspective, this is a familiar concept and one that has been central to the proliferation of bureaus across the globe over the last 15 years. It has been very successful in ensuring that emerging markets have the necessary financial infrastructure to support the growth of MSMEs and SMEs, to provide banking stability and deliver access to regulated financial services for all rather than it just being the reserve of the wealthy middle classes.
Private international investment is at the heart of this partnership with government by creating a sturdy financial infrastructure and sharing technical knowledge with local institutions. This is closely overseen and regulated by the governments and central banks with further support given by the World Bank. Creditinfo has been one of the leading global experts that has made significant investments in setting up new credit bureaus in green field markets under the regulation of local central banks.
The support of governments has been critical to accelerate access to finance for the “invisible” unbanked by introducing regulation to require the inclusion of “alternative data” such as utility data and mobile or nano loans. The benefit of this is that it enables a broad section of the population to create a financial footprint upon which they can build a credit history for the future. This was further endorsed by recent research from the PERC group.
The relationships between businesses and governments should see the development of new solutions to support SME and MSME growth as companies of this size are the backbone of many economies, especially in developing markets. Government departments will often have registers of companies which can be used in supervised environments to facilitate improved assessment of loans or credit making it faster and easier for SMEs to access financial support.
Government-investor partnerships may be seem like new vision emerging from the pandemic when state support was essential, however, for investors like Creditinfo that have been working within such a framework for many years, it is a proven method to achieve social, economic and business goals.
How to build an impeccable credit history

Within the first days of our lives, we are all issued a birth certificate which becomes the first document of the pile that we are to collect during our lifetime. Birth certificates are followed by passports, then graduation certificates, college or university diplomas. Reaching the age of majority entails, among other things, responsibility not only for one‘s professional career, but also for financial decisions which are reflected in the credit history. In other words, credit history is a yearbook of one‘s financial obligations, which is read by banks, leasing companies or other institutions in order to assign you to the categories of either reliable or less reliable clients and decide whether they are willing to accept you for credit.
No Credit Without Credit History
According to the surveys, more than half of the adult population of Lithuania are active users of credits to finance purchase of the real estate, vehicles, household appliances, furniture, PCs, phones, etc.
To get a credit, you apply to the banks or leasing companies. They first look into your credit history which shows how well you performed our financial obligations in the past, including consistency of timely payments for electricity, telecommunication services or garbage removal, also timely repayment of other credits and any overdue debts.
A good or bad credit history determines whether you will be accepted for credit to buy a new refrigerator instead of an old broken one, whether sellers will agree to sell you a new phone just after signing an agreement on payment in installments over the next two years. If the credit history is sound, you can expect the most favorable conditions and trust of the seller. A poor credit record means that you may have to pay the entire amount at once.
A History of Amounts and Discipline
The credit history reflects two types of information. The first one is an account of financial obligations, credits in the banks, consumer loans from credit institutions or peer-to-peer lending platforms, leasing, etc. Lenders use this information to assess the client‘s budget sufficiency, i.e., the percentage of income spent for servicing the existing debts. The second type of information is the track record of repayment of debts indicating the discipline of making payments for credits, mobile phone, internet, cable TV and other bills.
Banks Favor Positive Rather than Empty Credit History
The staff of the credit bureau is often asked what a good credit history is. One may think that lenders favor those who never had a loan, leasing or credit card, and never delayed payments to service providers, hence their credit history is empty. Yet the lenders‘ approach is different. On the one hand, an empty credit record may indicate that you had no need to borrow or to buy on lease in the past. On the other hand, who is more trustworthy: a client who repaid his lease or loan in time, or a person who never had any financial obligations? A survey conducted by “Mano Creditinfo“ revealed that banks tend to be more favorable towards clients who had financial obligations in the past as they are more predictable.
Financial institutions tend to trust clients with good credit history and offer them better conditions, such as a lower down payment, lower interest rate and more flexible repayment terms. For instance, Swedbank‘s Institute of Finances earlier advertised that good credit history may save up to several thousand euros in interest on home loans. Good credit history will save you up to EUR 500 on a loan for a EUR 5,000 worth car, or up to EUR 1,700 on a EUR 10,000 worth car lease.
Can You Fix a Bad Credit History?
Yes, you can, but it will take time and effort. There are several factors that determine a bad credit history, including high financial obligations, excessive and unreasonable borrowing, borrowing to service outstanding debts, delayed payments and other. If your credit history contains any such events, you have to brace yourself for a hard time, as cosmetic adjustments will not erase or eliminate them. If you tend to assume too many financial obligations, you will have to reduce their number and curb your appetite for borrowing for some time at least. If you have any overdue payments, you are recommended to make the payments as soon as possible and never delay them again.
Financial institutions usually analyze the credit history of the recent 2 or 3 years, and the negative impact of the sins of the past gradually fades away over time. Thus, if you have a poor credit history and decide to change your approach towards your financial obligations today, financial institutions may still have questions about your past financial behaviour for a couple more years to come.
Mistakes to be Avoided
Information about the financial relations and obligations will accompany you throughout your entire life telling a story of either a high financial discipline or lack of it. If you decide to borrow, you must carefully assess your ability to cover the debt and think about the ways to ensure the repayment even if you lose your income. Negative records appear in your credit history very quickly, within a month from the day the payment was due. Erasing this record from your credit history will take years, though.
Aurimas Kačinskas,
CEO – Creditinfo Lietuva.
Creditinfo invites the strongest companies to join the effort of making Lithuania greener

Green Parks of the Strongest Companies to Flourish in Lithuania
This year the Strongest will have an opportunity to contribute directly to the building of a greener Lithuania and to enter their names in the parks of the Strongest in Lithuania. Creditinfo shall plant a tree for each certificate awarded to the financially strongest companies. A new park of oak, maple, birch and linden trees will be planted in one of the busiest roundabouts between the Gerosios Vilties, Laisvės and Savanoriai streets in Vilnius this autumn.
The initiative of the credit bureau has received support from the Vilnius City Municipality. According to the Municipality, there are still many public areas in Vilnius which need to be planted, meanwhile the increasing population of the city drives the necessity to create as many green areas as possible.
“We welcome the initiative of Creditinfo to contribute to the making our city more beautiful and we support their idea of planting trees at one of the busiest roundabouts that is crossed by tens of thousands of citizens and visitors of Vilnius every day,“ says Remigijus Šimašius, the Mayor of Vilnius. “We are glad to see that the strongest companies in Lithuania make active contribution to the improvement of the environment around us.“
Creditinfo awards the Strongest in Lithuania certificates to the companies that are selected for their outstanding financial indicators, including appropriate payment of taxes, timely discharge of obligation towards employees and business partners, and sound financial discipline. Every year Creditinfo assesses businesses against over a hundred of different indicators and nominates up to 2.5 thousand of the strongest companies in Lithuania. Over 11 years of certification, the title of the Strongest in Lithuania has been awarded to over 20 thousand companies.
“This year the Strongest in Lithuania certification follows the principle Strong Companies Make Strong Decisions. Society expects contemporary companies to demonstrate comprehensive leadership in all walks of life. It is extremely important not only to secure financial stability of a company, but also to put into practice social responsibility and take care of the public good,“ says Aurimas Kačinskas, CEO of Creditinfo Lietuva. “We invite companies to join the effort of building a stronger and greener Lithuania.“
According to the CEO of the credit bureau, the capital city of Vilnius has been chosen to be the first to see the planting of the Strongest in Lithuania park. The traffic in Vilnius is heavy, making the quality of the air a high priority, therefore the first Strongest in Lithuania park is to be planted in the busy Gerosios Vilties roundabout. In the future, Vilnius may be followed by other cities and towns, depending on the involvement of the strongest companies in the initiative.
The Value of the Certificate is Higher this Year
The CEO of the credit bureau points out that this year the companies awarded with the Strongest in Lithuania certificate have a strong reason to be proud of sustainability of their activity. “Not all businesses have managed to secure their financial stability during the pandemic, therefore this year the award of the certificate recognizes the ability of businesses to weather a crisis and flexibility to adjust to the exceptionally complex conditions,“ says A. Kačinskas. “To distinguish companies with sound financial discipline, we will have their names written on the special memorial stand to be put up in the park.“
About the Strongest in Lithuania certificate
The credit bureau launched the Strongest in Lithuania certification in 2010, and this year counts the 11th season of certification already. The Strongest in Lithuania is the only recognized business credibility certificate in the Baltics with the longest history of existence. Over the decade, more than 15,000 Lithuanian companies have earned the right to use the certificate as a proof of their good financial reputation. Upon decision of Creditinfo Lietuva, this token of high credibility is awarded to companies with outstanding professional management practices, i.e. those that generate stabile income and profit, pay taxes and fulfil obligations to their partners on time, and have no debts.
Creditinfo Group becomes sole owner of International Bureau of Credit Histories in Ukraine

Creditinfo is investing in IBCH to improve its credit information sharing system
KYIV, UKRAINE, May 24, 2021 – Creditinfo Group, the leading global credit information and fintech services provider, today announces that it has become the sole owner of Ukraine’s International Bureau of Credit Histories (IBCH). Creditinfo aims to improve access to financial services for Ukrainians and support financial institutions with a full suite of best-in-class credit risk management tools.
Established in 2006, IBCH is one of three main credit bureaus in Ukraine. It offers a portfolio of products and solutions for credit risk management, expanding business opportunities, preventing fraud risks and NPL management improvement. Also, IBCH gives access to credit histories for individuals and legal entities.
“This investment shows Creditinfo’s renewed commitment to both the IBCH and Ukrainian financial market overall,” commented Seth Marks, Managing Director, Creditinfo Central & Eastern Europe. “We have been a partner of IBCH since launching in Ukraine. We have also established our credentials in more than 30 countries, also in the region, opening bureaus in Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan and the Baltics. We hope that this new investment and our wealth of international experience will help us further entrench IBCH and the Creditinfo brand in the Ukrainian financial services space as we partner with lenders to drive financial access through the use of best practices in credit risk management and data protection. Ukraine is an ever-evolving and developing market with considerable growth potential. We are eager to play a role in aiding this growth.”
Kateryna Danylchencko, IBCH General Manager, added, “this is a new important step forward for IBCH. Our team is energised by the opportunity to be a part of Creditinfo, and we hope to utilise the company’s expertise to assist us in the introduction of new products and services.”
About Creditinfo
Established in 1997 and headquartered in Reykjavík, Iceland, Creditinfo is a provider of credit information and risk management solutions worldwide. As one of the fastest-growing companies in its field, Creditinfo facilitates access to finance, through intelligent information, software and analytics solutions.
With more than over 30 credit bureaus running today, Creditinfo has the most considerable global presence in the field of credit risk management, with a significantly greater footprint than competitors. For decades it has provided business information, risk management and credit bureau solutions to some of the largest, lenders, governments and central banks globally to increase financial inclusion and generate economic growth by allowing credit access for SMEs and individuals.
For more information, please visit www.creditinfo.com
Media Contacts:
Caterina Ponsicchi
Group Marketing Director




