Creditinfo Launches ESG Hub to Fast-track Baltic Companies’ Access to Reliable Sustainability Data

New one-stop-shop solution aggregates information from more than 20 external sources, helping banks and businesses boost their ESG strategies, manage risk, and streamline their supply-chain transparency.
Creditinfo unveiled ESG Hub, the Baltic region’s first pan-regional platform that gives lenders and businesses instant, standardised access to the environmental, social and governance (ESG) data they need to comply with regulations, assess counterparties and execute sustainability strategies.
Building on Creditinfo’s long track-record of turning complex business information into accessible actionable insight, ESG Hub consolidates data from 20-plus public and proprietary data sources from Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania into one standardised API feed and ready-to-use report. By merging country-specific registries into a single, harmonised view, the platform lets banks and businesses manage ESG data uniformly across all three markets. Users can pull company-level metrics—from carbon emissions and energy intensity to board diversity and community impact—within seconds, eliminating the need to piece together separate national datasets manually.
“We want to accelerate the sustainability journey for the Baltic economies, and it all starts with easy access to trusted information. Until now, assembling ESG data has been difficult and time-consuming; companies have spent substantial time on these tasks, and the process has been inefficient,” said Elari Tammenurm, Regional Director, Continental Europe at Creditinfo. “With ESG Hub, any financial institution or company can integrate harmonised data directly into their existing workflows, cutting cost and complexity while improving decision speed.”
Proven model, now scaled to the Baltics
Creditinfo first introduced an ESG data service in Iceland in 2023; rapid adoption by local banks and corporates highlighted the growing importance of reliable sustainability intelligence. “The strong uptake we saw in Iceland showed us how big the need is,” noted Reynir Smári Atlason, Managing Director of Sustainability at Creditinfo. “We’re now bringing those learnings, and a richer dataset, to the Baltic markets.”
The company will continue to expand ESG Hub’s data source coverage and analytical modules over the coming months. Future roll-outs in additional Creditinfo markets are also planned.
For more information visit ESG Hub
Creditinfo & Little App Partner To Enhance financial Inclusion In Kenya
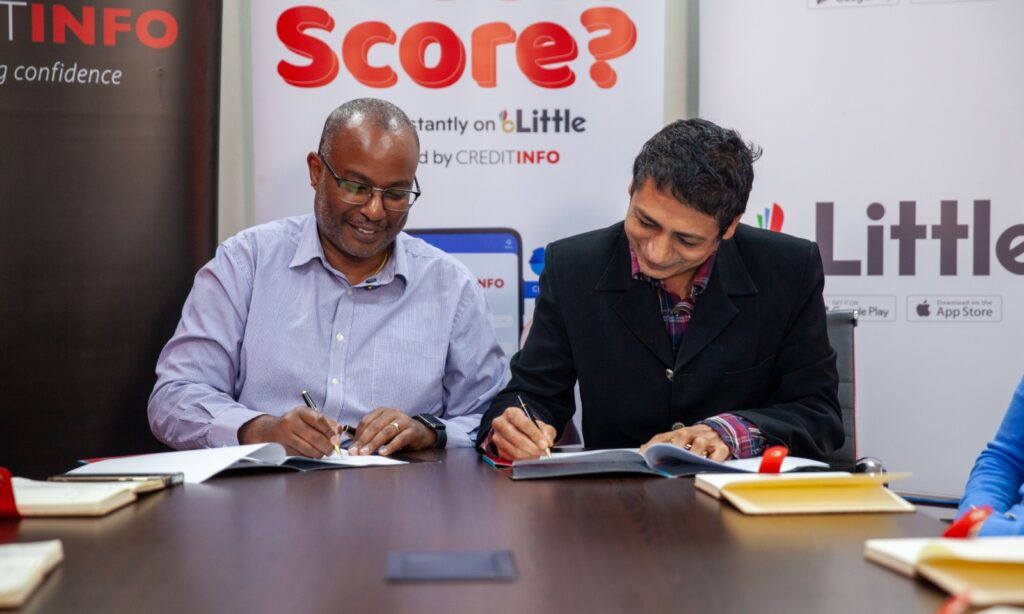

Little App’s new feature gives individuals and businesses instant, on-the-go access to their credit information
Nairobi, 18th June 2025 – Creditinfo, a global service provider for credit information and risk management solutions, has partnered with Little App, one of Africa’s most forward-thinking super apps, to enable Little App users to access their credit reports and monitor their credit scores instantly and securely within the app’s Financial Services section.
With the integration of Creditinfo’s credit bureau data into the app, individuals and businesses can conveniently view their credit information through their mobile devices. Whether applying for a loan, improving creditworthiness, or monitoring one’s financial health, this new feature makes it simple, fast, and user-friendly. Having this information available in one place will help people in Kenya to take control of their finances, make more informed decisions, and access credit with confidence.
“Our partnership with Little reflects more than just a shared goal; it’s a concrete step toward increasing financial inclusion and transparency across Kenya and the African region in the foreseeable future. Data is key to unlocking financial opportunity for people, and our priority is to make access to real-time, reliable credit information simpler and more intuitive. We’re immensely proud to deliver a solution that brings tangible benefits to people’s financial journeys,” said Kamau Kunyiha, Regional CEO East and Southern Africa at Creditinfo.
Kamal Budhabhatti, CEO at Little said: “Africa is undergoing a remarkable digital evolution, with mobile technology transforming how people live and engage with services. Through our collaboration with Creditinfo, we’ve built a solution that meets people where they are – on their phones – and fits seamlessly into their daily lives. We want to demystify complex financial data for everyone, empowering users to make informed decisions while driving lasting social and economic impact.”
-END-
About Creditinfo
Established in 1997 and headquartered in London, UK, Creditinfo is a provider of credit information and risk management solutions worldwide. As one of the fastest-growing companies in its field, Creditinfo facilitates access to finance, through intelligent information, software and decision analytics solutions.
With more than 30 credit bureaus running today, Creditinfo has the most considerable global presence in this field of credit risk management, with a significantly greater footprint than competitors. For decades it has provided business information, risk management and credit bureau solutions to some of the largest, lenders, governments and central banks globally to increase financial inclusion and generate economic growth by allowing credit access for SMEs and individuals.
For more information, please visit www.creditinfo.com
About Little
Little App is a pan-African super app that has been transforming everyday experiences since 2016. With nearly a decade of innovation, Little offers a wide range of tech-driven solutions across mobility, payments, delivery, healthcare, and lifestyle services.
Operating in multiple African countries, Little serves both individual users and organizations—delivering convenience, affordability, and efficiency. From ride-hailing to enterprise transport solutions and digital wallets, Little is at the forefront of enabling digital and financial inclusion across the continent.
For more information, please visit www.little.bz
Creditinfo Kenya and Kamoa Join Forces to Expand Access to Credit Through Alternative Data
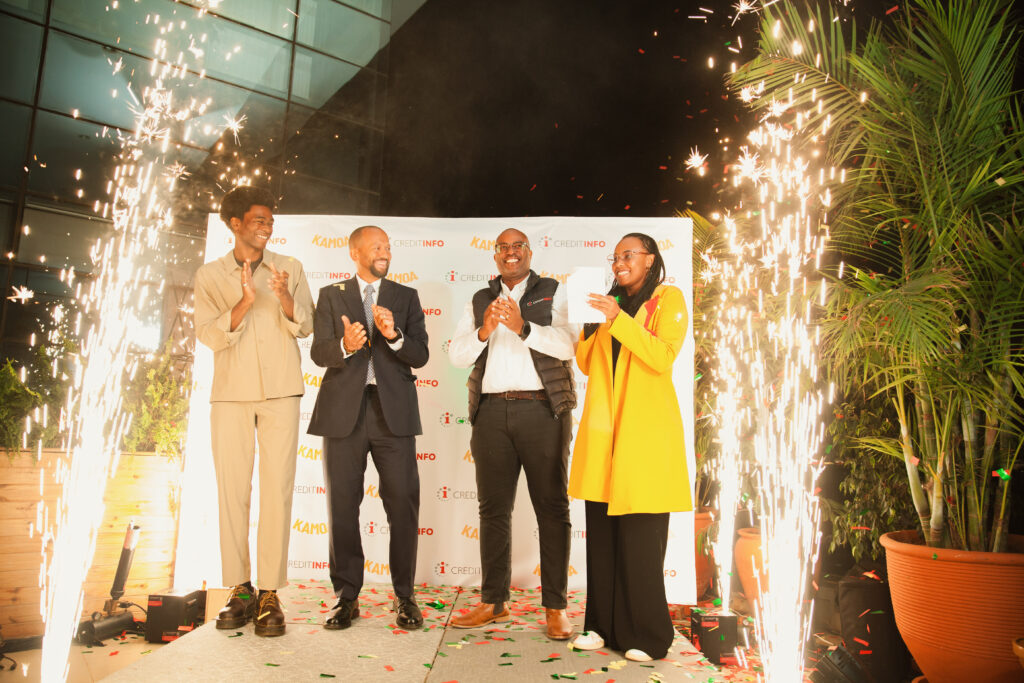

NAIROBI, Kenya – June 13, 2025 – Creditinfo Kenya (CIK), a credit information and risk management solutions provider, and Kamoa have announced a strategic partnership to improve credit decisioning and financial inclusion in Kenya.
The partnership will see Creditinfo Kenya leverage Kamoa’s alternative data technology to build more comprehensive credit profiles for individuals and SMEs. This approach aims to unlock lending opportunities for both the banked and underbanked, while enhancing the quality and inclusiveness of credit assessments.
Through this collaboration, Creditinfo Kenya and Kamoa aim to:
- Accelerate financial inclusion,
- Support the growth of SME lending
- Enable lenders to make more accurate, data-driven decisions
‘At Creditinfo, we’re committed to broadening access to financial services for individuals and businesses. Our partnership with Kamoa marks a key milestone in improving credit decisioning and inclusive financial solutions in Kenya. By using broader data, lenders can make smarter lending decisions, enabling more people to access the financial services they need to grow and prosper financially. Together, we’re setting a new standard in credit decisioning while fostering financial empowerment across Kenya,” said Kamau Kunyiha, Regional CEO East and Southern Africa at Creditinfo.
The agreement marks a significant step toward a more inclusive and data-enriched credit ecosystem in Kenya.
FIND THE WHITE PAPER HERE – Boosted Score - White Paper
-END-
About Creditinfo
Established in 1997 and headquartered in London, UK, Creditinfo is a provider of credit information and risk management solutions worldwide. As one of the fastest-growing companies in its field, Creditinfo facilitates access to finance, through intelligent information, software and decision analytics solutions.
With more than 30 credit bureaus running today, Creditinfo has the most considerable global presence in this field of credit risk management, with a significantly greater footprint than competitors. For decades it has provided business information, risk management and credit bureau solutions to some of the largest lenders, governments and central banks globally to increase financial inclusion and generate economic growth by allowing credit access for SMEs and individuals.
For more information, please visit www.creditinfo.com
About Kamoa
Kamoa is a data technology company on a mission to unlock access to finance and financial opportunity across Africa. We harness the power of data to help individuals, small businesses, and financial institutions make smarter, more inclusive decisions. By building intelligent systems that connect and interpret diverse data sources, we aim to close information gaps and enable better financial outcomes across lending, savings, insurance, and beyond.
Founded in 2023, Kamoa began in stealth with a bold ambition: by 2030, to become a leading infrastructure layer for financial innovation across the continent — empowering players from microfinance institutions to major banks, and serving customers from every corner of the market.
For more information, please visit https://kamoa.app/enterprise
Creditinfo launches new platform to boost African businesses’ access to credit and global opportunities
Creditinfo’s Business Information Platform Africa aims to strengthen local economies and foster global partnerships
London – 14 May 2025 – Creditinfo has today announced the launch of Business Information Platform Africa (BI Africa) to help African businesses and financial services access trade credit more easily and build stronger relationships with global partners. The platform will be rolled out in Kenya in June, with more markets to follow.
The move builds on Creditinfo’s success in the Baltics, where its business information tools have helped companies navigate partnerships and manage risk for over a decade. Now, that same model is being brought to Africa – starting with Kenya – where access to verified, independent business data has often been a challenge.
‘This launch isn’t just about data. It’s about unlocking opportunity,’ said Satrajit Saha, CEO at Creditinfo. ‘When businesses have the right information at their fingertips, they can make smarter, faster decisions that drive growth, close more deals and build lasting confidence – both locally and globally.’
The BI Africa platform offers reports on over one million African companies, presented in a simple, globally standardised format. Users can check key facts about potential partners or customers, everything from credit health to company history, making it easier to assess risk and build trust. Additionally, as an added service, Kenyan businesses will have access to company reports on over 430 million international companies – empowering them to confidently verify both new and existing clients through Creditinfo and its network of global partners.
‘We want to make it easier for African businesses to prove their value, compete globally, and grow with confidence,’ added Saha. ‘Greater transparency leads to stronger trust and improved access to finance – benefits that extend across economies and communities. And that’s a win for everyone.’
It also includes a Manual Investigation Service for those who need deeper insight. Users can request tailored research into specific companies, providing information that goes beyond the numbers, like ownership structures, litigation history, or up-to-date financials. Crucially, the platform isn’t just for large institutions. It’s been designed to support SMEs and individual entrepreneurs, too – those who often struggle the most with gaining access to trade credit.
‘By bridging critical trust and information gaps, our robust platform will redefine what is possible for businesses, of all sizes, in Kenya and beyond. What once took three to five working days to verify a potential business partner can now happen in seconds, without compromising on regulatory compliance. That’s a game-changer for companies, particularly in the SME sector, who need to make quick decisions in competitive markets,’ said Kamau Kunyiha, Regional CEO East and Southern Africa at Creditinfo.
-END-
About Creditinfo
Established in 1997 and headquartered in London, UK, Creditinfo is a provider of credit information and risk management solutions worldwide. As one of the fastest-growing companies in its field, Creditinfo facilitates access to finance, through intelligent information, software and decision analytics solutions.
With more than 30 credit bureaus running today, Creditinfo has the most considerable global presence in this field of credit risk management, with a significantly greater footprint than competitors. For decades it has provided business information, risk management and credit bureau solutions to some of the largest, lenders, governments and central banks globally to increase financial inclusion and generate economic growth by allowing credit access for SMEs and individuals.
For more information, please visit www.creditinfo.com
The Importance of Trust in Digital Interactions: The Cornerstone of a Digital Economy

There’s a diversity in maturity in digitization across the globe – from markets that are almost universally digital, through markets with developing digital economies, to markets with embryonic digital ecosystems. Mature economies typically have more mature controls but remain attractive to fraudsters because of the scale of opportunity – emerging digital economies typically have less robust ecosystems and are attractive because of the inherent vulnerabilities in the controls – with a promise for future growth.
The anonymity and distance that digital platforms afford make it easier for fraudsters to operate undetected.
For bad actors, the business model is scalable – in a digital economy the unique skills of Frank Abagnale Jr (of “Catch Me If You Can” fame) become redundant. The ready availability of personal data through vast data breaches and social engineering, and online access to digital channels present an attractive proposition for the enterprising fraudster.
In fact, cybercrime has risen dramatically alongside digital transformation, with fraud rates increasing globally – and we’re increasingly seeing collaboration between cybercrime, fraud, organised crime and money laundering. Organizations face mounting challenges in protecting their digital infrastructure and customers from fraudulent activities. From identity theft to financial scams, fraudsters are leveraging a wide array of tactics to deceive individuals and organizations.
The digital economy’s vulnerability to fraud presents significant risks, not only for organizations, but also for consumers. When fraud occurs, it undermines the trust that is essential to the functioning of the digital economy. If consumers and businesses cannot trust the digital services they engage with, it will slow adoption, hinder growth, and damage reputations. Therefore, mitigating fraud risk is not just about protecting individual interactions – it’s about maintaining the integrity of the entire digital ecosystem.
The importance of trust in digital interactions cannot be overstated. From e-commerce to financial services and beyond, trust is the foundation upon which all successful digital interactions are built. At the core of this trust is the concept of identity verification. In a world where interactions are increasingly conducted online, it’s critical to ensure the presented identity is a real-world identity, not synthetic – and that the individual presenting the identity is the owner of that identity.
The need to assert identity in digital engagements goes beyond basic security – it forms the bedrock of confidence that drives the entire online ecosystem. Whether consumers are signing up for a new banking service, purchasing products, or enrolling in educational courses, verifying the authenticity of their identity is paramount. Identity verification serves not only to protect individuals but also to secure businesses from fraudulent activities, which, in turn, strengthens the broader digital economy.
The Role of Identity Verification in Mitigating Fraud Risk
At the heart of reducing fraud risk lies robust identity verification. This process ensures that the individual engaging with a digital platform is who they claim to be. It is a crucial step that lays the groundwork for every subsequent transaction, providing a layer of protection for both consumers and businesses. Without reliable identity verification, any digital interaction is susceptible to being manipulated by malicious actors.
Identity verification can be achieved through a variety of techniques, including biometric verification, document verification, and multi-factor authentication. These methods allow businesses to verify that a person is genuine, providing them with the confidence to proceed with transactions. This, in turn, enables a safer and more reliable digital environment for everyone involved.
However, while basic identity verification is a critical first step, it is only part of the solution.
The Power of Layering Fraud Defences
In a digital economy, an identity is far more than a name, address, date of birth and national id number.
From basic digital identity attributes such as mobile numbers, email addresses and IP addresses, through payment attributes such as bank details and credit card numbers, through connected messaging apps and service accounts, through device attributes such as screen size, make, model, time zone, location, installed apps, through biometric attributes such as facial patterns, to behavioural attributes such as physical device interactions. A digital identity is an extensive and interconnected web of many attributes.
The real strength in mitigating fraud risk lies in combining multiple layers of defence – a multifaceted approach that examines not only the traditional identity attributes, but the wider digital footprint and the connections between attributes across the identity graph. Consistency and conformity to normalised patterns help establish greater trust – inconsistency and anomalous patterns indicate greater risk. Machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques are increasingly used to examine attribute patterns – generating increasingly performant models.
The power of a layered approach lies in managing the balance between making life difficult for bad actors and removing friction in genuine interactions. In a digital economy consumers become increasingly intolerant of any friction in their interactions with organisations. Where consumers encounter even minor friction, they will abandon the sales process and look for alternative providers – in a competitive market, the winners will be the businesses who deliver the easiest way to interact – but without appropriate fraud defences, success will be short lived.
More accurate multifaceted risk assessments can be implemented based lighter data capture, drawing insights from a broad range of sources, reducing CX friction and abandonment, readily securing greater trust, more accurately exposing risk.
Summary
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, organizations must prioritize trust as the cornerstone of their interactions with consumers. Robust identity verification and a layered approach to fraud prevention are not just best practices – they are essential for maintaining the integrity of the digital economy. By effectively combining multiple layers of defence, businesses can balance security with convenience, reducing fraud risk without sacrificing customer experience. In the end, fostering trust in digital engagements is the key to enabling sustained growth and success in an increasingly complex and competitive online ecosystem.
For more information, please visit: www.creditinfo.com
or email info@creditinfo.com
Author : Robert Meakin – Director, Fraud & ID, Creditinfo Group
Creditinfo Launches New Global Fraud & ID Solution

Creditinfo’s new solution supports clients in mitigating the impact of fraud and supporting organisational growth.
London – 27th March 2025: Creditinfo, a global service provider for credit information and risk management solutions, has today announced the launch of its global identity, know your customer (KYC), and fraud and ID solution, set to help organisations tackle financial crime.
The overall global economic impact of financial crime has been estimated to be $5 trillion. What’s more, according to the 2024 Nasdaq global financial crime report, fraud losses totalled $485.6 billion worldwide, from fraud scams and bank fraud schemes alone. As such, organisations face a series of challenges, from eroding profit margins to reputational risks to data breaches. Creditinfo’s solution helps organisations to address these challenges by using credit bureau data, government information services, and other registries to establish trust in presented identities, without negatively impacting the customer experience.
The solution integrates identity proofing, digital risk signals and comprehensive international and domestic watchlists to deliver strong KYC compliance and reduce the risk of fraudulent activity. It also enables businesses to streamline risk management and ensures they meet stringent customer due diligence requirements under anti-money laundering (AML) regulations.
As a global solution, it is tailored to meet the unique needs and maturity-levels of different markets. By accounting for these differences, organisations that use the solution can adapt their fraud prevention strategies to specific local risks, strengthening security and promoting financial inclusion.
Creditinfo has appointed Rob Meakin as Director of Fraud & Identity to head up this service. He brings extensive experience in fraud prevention, identity management, and financial services. Meakin will lead efforts to help organisations counter fraud – leveraging advanced technologies and data analytics to enhance the customer experience and strengthen fraud and AML controls.
Rob Meakin, Director of Fraud and Identity at Creditinfo, said: “The growing presence of organised financial crime is significantly hindering economic growth on both a local and global scale, costing businesses huge sums of money each year – in fraud losses, lost sales and operational costs. That’s why, at Creditinfo, we’re pioneering a solution that provides a way for organisations to manage risk and maintain compliance while facilitating secure and easy access to financial products and services for consumers.”
John Cannon, Chief Commercial Officer at Creditinfo said: “By removing friction from both traditional and digital onboarding and origination processes, our solution helps organisations reduce fraud, improve conversion rates, and drive top-line growth while ensuring a seamless customer journey. As we strive to expand our global reach and enhance financial access for millions of consumers and businesses worldwide, having Rob join our team is an invaluable advantage, strengthening both our security capabilities and our ability to deliver innovative solutions.”
-END-
About Creditinfo
Established in 1997 and headquartered in London, UK, Creditinfo is a provider of credit information and risk management solutions worldwide. As one of the fastest-growing companies in its field, Creditinfo facilitates access to finance, through intelligent information, software and decision analytics solutions.
With more than 30 credit bureaus running today, Creditinfo has the most considerable global presence in this field of credit risk management, with a significantly greater footprint than competitors. For decades it has provided business information, risk management and credit bureau solutions to some of the largest, lenders, governments and central banks globally to increase financial inclusion and generate economic growth by allowing credit access for SMEs and individuals.
For more information, please visit www.creditinfo.com
For inquiries email rob.meakin@creditinfo.com
Download Brochure HereConstruction sector in Lithuania twice as risky as other businesses

Despite rising incomes and headcount, seizures amount to almost EUR 110 million
19% of construction companies are in the high and top bankruptcy classes and 31% are at risk of late payment, according to a recent study by Creditinfo Lithuania. Despite the number of employees and the rapid growth in revenues, the sector has already recorded 169 company bankruptcies this year. Nearly 11,000 debts have been registered, totaling more than €91 million. 1049 companies are subject to asset seizures amounting to almost €110 million.
There are currently 19850 construction companies registered in Lithuania, employing a total of almost 110 000 workers. At the beginning of this year, the number of companies in the sector was 20367, creating 108.2 thousand workplaces, while in 2023 the figures were 19167 and 107.7 thousand respectively.
According to data provided to the Centre of Registers, in 2023, construction companies in Lithuania together generated revenues of more than EUR 10.6 billion, representing 14.7% of the country’s GDP. In comparison, in 2022, construction companies’ gross revenues were 22.6% lower at EUR 8.7 billion.
Following the data provided by the companies, the top ten construction companies in terms of revenue in 2023 are Kauno Tiltai (EUR 192.9 million), YIT Lietuva (EUR 191.1 million), Fegda (EUR 184.2 million), Conres LT (EUR 117.3 million), Infes (EUR 107.3 million), Green Genius (EUR 102.7 million), “Merko statyba (EUR 97.8 million), Žilinskis & Co (EUR 94.4 million), Autokausta (EUR 94.3 million), Stiemo (EUR 87.4 million).
Despite the year-on-year increase in revenues, the construction sector is twice as risky as any other business in Lithuania. Currently, 19% of construction companies are in the high and highest bankruptcy classes, while almost one third (31%) are at risk of default. The sector has a similar risk profile from the beginning of 2023. Over the last 5 years, the highest risk levels were reached in 2020 and 2021, when a quarter of construction companies were close to bankruptcy and almost half of the companies (47%) were at risk of default.
In comparison, the average riskiness of all Lithuanian businesses is twice as low: 9% of companies are in the high and highest risk classes, while 16% are at risk of default.
Since 2007, 4,497 construction companies have gone bankrupt in Lithuania, with an average of 254 each year. The highest number of bankruptcies was recorded in 2009, when 445 companies became insolvent. This year, 169 construction companies went bankrupt between January and September.
The average amount of seized assets increased by 34.7% to EUR 105 thousand
Currently, 10892 debts of construction companies are registered in the credit bureau system, with a total amount of EUR 91 million and an average debt of EUR 8 360. Compared to the beginning of January 2024, the number of debts exceeded 13,000, the total amount was €164 million, and the average debt size was 1,5 times higher (€12,602).
According to the data of the Credit Bureau, there are currently 2209 seizures on construction companies, including 1043 seizures with monetary value, for a total amount of EUR 109.8 million. The number of construction companies with at least one attachment is 1049 and the average attachment per company exceeds EUR 105 000. At the beginning of this year, the number of seizures was 2,702, with 1,293 seized companies, and the average amount of a single seizure was EUR 68.7 thousand, 1/3 (34.7%) lower than at present.
“If you notice in the credit bureau’s systems that a business partner or client has seizures, please be careful. It is a serious sign that the company is at risk of defaulting on its payments,” advises Rasa Rasickaitė, Risk Assessment and Management Expert at Creditinfo Lithuania. Asset seizure is a compulsory restriction of the ownership right to property, which can be applied by state authorities to secure evidence, civil action, possible confiscation of property, as well as the collection of fines and unpaid payments, satisfaction of creditors’ claims, and fulfilment of other claims and liabilities. Therefore, when you see a registered seizure, you should also pay attention to other available information, such as court information, debts to creditors, the tax authorities and the social security system.”
According to Rasickaitė, in the event of a seizure of assets, it is advisable to find out the reason for which the seizure has been registered, what assets have been seized, and whether the seized assets are allowed to be disposed of in the course of the company’s business. If there are doubts about the ability of the business partner to pay, it is advisable to ask for prepayment or guarantees.
Can Expanding the Role of CRBs Through Trade Data Sharing Enhance Business Credit and Improve Cash Flow Management?

There is a growing need to expand the information shared with Credit Reference Bureaus ( CRBs) to include trade data. Many manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers have reported cash flow challenges due to difficulties in recovering debts from their customers. This often results in their ability to restock or pay suppliers, further straining their operations. In Kenya, trade agreements frequently rely on informal arrangements, with limited legal recourse due to delays in the judicial systems. Could CRBs play a more significant role in addressing these issues?
As businesses increasingly rely on data to drive decision-making, it’s evident that CRBs, which currently hold financial data related primarily to bank and mobile loans, could greatly enhance their scope. While the inclusion of traditional credit data has boosted financial inclusion, expanding this to cover trade credit information especially from manufacturers, service providers, and wholesalers could revolutionise how businesses extend and manage credit.
If this trade data were collected and shared under a regulatory framework, it could enhance credit trading, improve business relationships, and further financial inclusion. Regular purchasing and payment data, when synthesized, could help businesses evaluate potential customers, set credit limits, and make informed decisions beyond traditional borrowing data.
Accounts receivable teams often struggle to recover overdue debts from customers extended credit without proper risk assessment. Introducing legislation to compel specific entities to share trade data based on factors like turnover or invoice value could help manage risk, reduce legal disputes, and cut down on costs associated with unpaid receivables.
Moreover, the Kenya Revenue Authority could benefit from improved tax collection, as greater financial discipline would be encouraged to avoid negative CRB listings, which can impact a company’s ability to do business. This would also help reduce the burden on the Judiciary, where countless civil cases related to unpaid debts remain unresolved, leading to significant business losses.
Properly managing and sharing trade credit information could streamline the business environment, improving cash flow and financial planning. Additionally, incorporating trade credit data into CRB decision making tools could help boost an individual’s or entity’s creditworthiness when seeking traditional loans. On an individual level, high value asset purchase, such as land and vehicles, could also be evaluated using shared credit sales and receipts data, providing both buyers and sellers with insights into the financial reliability of potential customers.
In conclusion, expanding the data shared with CRBs could significantly improve risk management, debtor control, and financial stability, creating a more transparent and efficient trading environment for businesses of all sizes.
By Francis Shikuku
Accounts Assistant, Creditinfo Kenya
Creditinfo appoints Charles De Winnaar as Global Head of Sales Strategy and Sales Operations

Former Marsh Africa Sales Leader – Charles De Winnaar – brings a wealth of sales and leadership experience to drive Creditinfo’s international growth
London – 26th September 2024: Creditinfo, a global service provider for credit information and risk management solutions, announces the appointment of Charles De Winnaar as its Global Head of Sales Strategy and Sales Operations. As an experienced sales leader in financial services, Charles will lead Creditinfo’s global sales strategy and operations across its network of 30 credit bureaus. He joins the company from Marsh Africa, where he held the position of Sales & Distribution Leader.
In his role, Charles will be responsible for Creditinfo’s revenue growth, market expansion, and operational excellence to ensure scalability and enhance the customer experience across its different markets. From developing strategic partnerships to driving innovation in sales processes and technologies, he’ll play a key part in the next phase of Creditinfo’s international growth.
With over two decades of experience in sales and finance, Charles has a deep understanding of global financial markets and an impressive history of leading large-scale sales teams, bolstering business growth, implementing customer-centric solutions and transforming sales operations.
As Sales Leader at Marsh Africa, he executed the revenue and portfolio optimisation strategy across multiple Africa regions. Prior to joining Marsh Africa, he held various sales leadership roles at the National Bank of Kuwait and Barclay’s Bank Africa. During his time at Barclays, he led the development and launch of a first-to-market mobile payment wallet lending solution in Africa.
Charles De Winnaar, newly appointed Global Head of Sales Strategy and Sales Operations at Creditinfo said: “I’m delighted to join Creditinfo, a company that is committed to empowering people and businesses through financial inclusion. I look forward to working with the talented global team and contributing to Creditinfo’s long-term success.”
Satrajit Saha, Global CEO at Creditinfo said: “With his unmatched expertise in global markets and a proven track record of building strategic partnerships across different regions, Charles is a valuable addition to our leadership team. As we look to accelerate market expansion, harness digital transformation in our global strategy, and continue to facilitate access to finance for millions of individuals and businesses worldwide, Charles will be instrumental in helping us to achieve these goals.”
Charles will report directly to Satrajit Saha, Creditinfo’s Global CEO.
-END-
About Creditinfo
Established in 1997 and headquartered in London, UK, Creditinfo is a provider of credit information and risk management solutions worldwide. As one of the fastest-growing companies in its field, Creditinfo facilitates access to finance, through intelligent information, software and decision analytics solutions.
With more than 30 credit bureaus running today, Creditinfo has the most considerable global presence in this field of credit risk management, with a significantly greater footprint than competitors. For decades it has provided business information, risk management and credit bureau solutions to some of the largest, lenders, governments and central banks globally to increase financial inclusion and generate economic growth by allowing credit access for SMEs and individuals.
For more information, please visit www.creditinfo.com
Central Bank of Seychelles awards Creditinfo contract to Develop and Implement a new Credit Information System (SCIS)

PRESS RELEASE
Victoria– September 11, 2024 – The Central Bank of Seychelles (CBS) has today launched the Seychelles Credit Information System (SCIS) in accordance with the Credit Reporting Act, 2023, to improve credit information sharing across the financial system.
The SCIS will be administered by CBS, which will be responsible for overall supervision of the operation of the system, as well as providing awareness on the system and its governing law. The contract to develop and implement the SCIS was awarded to Creditinfo CEE a.s., a company based in the Czech Republic, through an open bidding method as per the CBS procurement process in April 2021.
The SCIS – which replaces the previous Credit Information System established under the Credit Reporting Regulations 2012 – is an improved credit information system which will enhance credit reporting and data exchange between participating institutions. It incorporates automated features requiring minimal manual processing, hence mitigating potential risks of inaccuracies in the credit information of customers.
The current participants of the SCIS include the commercial banks, Seychelles Credit Union, Development Bank of Seychelles and the Housing Finance Company (HFC). The SCIS will continue to expand with the addition of other participants through a phased approach, to include Government entities, utility companies, hire purchase and credit sales, financial leasing companies, and insurance companies. The addition of these other entities – that are also engaged in activities that provide for payment arrangements – will give a more accurate indication of the repayment history and level of indebtedness of customers, information which is essential in the decision-making process for granting credit and loan facilities.
To note that only participating institutions can access the credit information of an individual, at the consent of the individual, in compliance with the Credit Reporting Act, 2023. Individuals holding accounts with these institutions will also be able to access their own credit report through the Customer Credit Portal, which is expected to be launched in the first quarter of 2025.
To watch a news clip of the event, click here.
Visit our websites for more information
ENDS.




