Creditinfo awarded contract as the service provider for the Credit Information System of Seychelles

Creditinfo to establish a new Credit Information System for the country.
London, UK – 11th January 2022: Creditinfo Group, the leading global credit information and decision analytics solutions provider, today announced that it has signed a contract to design, implement and support a new Credit Information System (CIS) for the Central Bank of Seychelles (CBS).
The contract – which will see Creditinfo’s solution rolled out over the next 12 months – makes CBS the 10th central bank to procure a credit information solution from the company.
At the end of 2020, the Seychelles population stood at 98,963, out of which there were approximately 20,099 active retail credit consumers. Seven commercial banks, all licensed and regulated by CBS, are currently the main institutions granting credit facilities to customers. A local credit union and two micro-finance institutions, also supervised by CBS, are the other major providers of credit facilities.
One of the recommendations in Seychelles’ Financial Sector Development Implementation Plan adopted in 2014 was the need to enhance the effectiveness of the existing CIS operated by CBS, inclusive of broadening the scope for the capture of information across all relevant credit providers. In this context, CBS initiated a tender process in April 2021, inviting credit information solutions providers to submit proposals to develop and implement a new CIS. The contract has ultimately been awarded to Creditinfo.
The solution will include scoring, benchmarking, and the implementation of external data sources. Creditinfo will also provide training, consultancy and ongoing support services for the management of the system over the next five years to ensure that CBS employees, local lenders and data providers have the necessary knowledge to make the new CIS a successful endeavor.
Once established, the new CIS will support existing lenders and, over time, onboard other credit data providers, including fintech companies, state-owned enterprises, hire purchase providers, credit sales and financial leasing companies, insurance companies, amongst others. Hence, the new and expanded CIS will support the incorporation of additional data to supplement traditional sources and ultimately provide more individuals and businesses with the financing needed to realize their goals and grow the economy. In addition, the enhanced system will assist the overall mitigation of credit risk.
Samuel White, Regional Director at Creditinfo commented: “While the Central Bank of Seychelles currently has a credit information system in place, it doesn’t meet the market needs of today, and certainly doesn’t enable it to realize the future ambitions of the country and its economy. We’re delighted to win this tender to put in place the technology and knowledge base to help open doors for individuals and small and medium-sized enterprises by increasing access to credit.
We see huge untapped potential in the market, and we are excited to work with our 10th central bank customer to establish a credit information system fit for the future. Once operational, this new system will enable more responsible lending by empowering local credit providers with the data they need to ensure they manage lending risks appropriately, ultimately boosting access to finance for individuals and small businesses.”
Caroline Abel, Governor, Central Bank of Seychelles, said: “Seychelles has a vibrant financial services ecosystem, and access to credit is an important aspect as we look to boost financial inclusion in the market and look at ways to grow our economy. At the same time, lenders should have access to appropriate data to have a better overview of the creditworthiness of borrowers, be able to assess credit risks and make sound financial decisions. Information collected through such a system can also be used for analysis and monitoring in the areas of financial inclusion and stability.
The CBS is therefore looking forward to the collaboration with Creditinfo over the next five years to have a modern credit information system that is in line with industry standards, ultimately assisting the development of the credit environment and overall financial sector.”
Paul Randall, CEO of Creditinfo Group added: “Creditinfo has been effective in strengthening the financial infrastructure in numerous countries across the world, and working with central banks to create a robust and fair way to assess risk and credit affordability. We are looking forward to supporting the Central Bank of Seychelles with their implementation of a future-looking credit information solution and widening access to the information and financing that will be key to future business and economic growth in the country.”
-ENDS-
About Creditinfo
Established in 1997 and headquartered in London, UK, Creditinfo is a provider of credit information and risk management solutions worldwide. As one of the fastest-growing companies in its field, Creditinfo facilitates access to finance, through intelligent information, software and analytics solutions.
With more than 30 credit bureaus running today, Creditinfo has the largest global presence in the field of credit risk management, with a significantly greater footprint than competitors. For decades it has provided business information, risk management and credit bureau solutions to some of the largest lenders, governments and central banks globally – all with the aim of increasing financial inclusion and generating economic growth by allowing credit access for SMEs and individuals.
For more information, please visit www.creditinfo.com
Media Contacts:
Matt Silver
Babel PR for Creditinfo Group
+44 (0)20 7199 3997
Creditinfo awarded license to become Malta’s first Credit Bureau

Creditinfo Malta will help local credit providers take a more intelligent approach to risk and boost financial inclusion.
London, UK – 21st December 2021: Creditinfo Group, the leading global credit information and decision analytics solutions provider, today announced that its Maltese business has been granted the license to act as a Credit Reference Agency, officially recognizing the Creditinfo Malta as the first licensed credit bureau in Malta.
This license will enable the company to launch a credit scoring system for Malta, and collaborate with local banks and lenders to create dedicated scoring products and strategies, tailored to their needs and risk appetite.
Consumers and SMEs in smaller markets like Malta are less likely to obtain financing than those in larger market with more established financial infrastructure, due to lack of information about their credit history. A credit reporting system – like the one Creditinfo is putting in place – helps to provide the information on borrowers and their financial situation lenders need to derisk the system and give them the confidence to widen access to financing.
The deal, which will see Creditinfo play an increasingly important role in the Maltese market, strengthens the company’s relationships with two key local authorities, the Malta Business Registry and the Malta Financial Services Authority, who are equally invested in growing the Maltese economy and boosting financial inclusion.
Clifford Debono, Country Manager of Creditinfo Malta commented: “A formalized credit reporting system in Malta should help open doors for small and medium-sized enterprises that have long been closed, by increasing access to credit. That will in turn enable them to grow, create jobs and benefit the overall economy.
“We see huge untapped potential in Malta, and we’re excited to establish the country’s first ever credit bureau, which will be a key driver of digitalization in Maltese financial services., ultimately boosting access to finance for individuals and small businesses.”
Paul Randall, CEO of Creditinfo Group added: “Creditinfo has been effective in strengthening the financial infrastructure in numerous countries across the world. We’re looking forward to seeing how the local lending landscape develops as we roll out our market leading credit bureau solution in Malta, derisking the financial system and widening access to the financing that will be key to future business and economic growth in the country.”
Ends
About Creditinfo
Established in 1997 and headquartered in London, UK, Creditinfo is a provider of credit information and risk management solutions worldwide. As one of the fastest growing companies in its field, Creditinfo facilitates access to finance, through intelligent information, software and analytics solutions.
With more than 30 credit bureaus running today, Creditinfo has the largest global presence in the field of credit risk management, with a significantly greater footprint than competitors. For decades it has provided business information, risk management and credit bureau solutions to some of the largest, lenders, governments and central banks globally – all with the aim of increasing financial inclusion and generating economic growth by allowing credit access for SMEs and individuals. For more information, please visit www.creditinfo.com
Media Contacts:
Matt Silver
Babel PR for Creditinfo Group Creditinfo@babelpr.com
+44 (0)20 7199 3997
New Creditinfo Jamaica Country Manager encourages Jamaicans to be proactive

Christopher R. Brown who was appointed as the new Country Manager for Creditinfo Jamaica on August 11, 2021, is encouraging Jamaicans to “be vigilant in guarding their credit history and their credit data and in managing them” to ensure there are no surprises when individuals or businesses seek to access services which require a credit report.
Brown, in an interview with the Jamaica Observer, reminded Jamaicans that they are entitled to one free copy of their credit report each year by law. He said Jamaicans should go to any of the credit bureaus and request their credit report each year and scrutinise it for “errors or outdated information” and where these are found, “they can then lodge a formal dispute after which it is the responsibility by law for the institution that they have lodged the complaint against, to investigate and correct it, once it is proven that it is an inaccurate record that is kept for that individual”.
He said errors can occur in the case where people may “have closed an account and completed payments on a loan account or a mortgage account, or a hire purchase agreement, and unfortunately it is not updated in the system and it is negatively impacting their credit score. So even after you have closed an account or some contract, or some credit cards or loans that you have paid, it is good to check to ensure those information are updated in the system so that your credit report is always current and up to date, because managing your credit is very essential in these days where credit is king and so fundamental to economic livelihood and, by extension, economic growth.”
He told Sunday Finance that if the entity against which the error complaint is brought, investigates and validates that there was an error, the law requires an updated credit report to be generated and dispatched to the institution which the individual had sought to do business with in the last six months. Whether terms or conditions of any agreements change after the updated information is then to be negotiated with the entity with which the individual is doing business. He stressed the importance of having the records updated because entries stay on the report for seven years.
Brown said getting Jamaicans to be vigilant in guarding their credit data is the message Credit Info Jamaica is pushing.
Credit Info Jamaica is the first credit bureau that was established in the country following the passage of the Credit Reporting Act in 2010. The company, which started its Jamaica operation in 2011, is part of a global network which has operations in Europe, Africa and sections of the Caribbean. In the region it also has facilities in Barbados, Guyana and the Eastern Caribbean.
“We see ourselves as an important part of the local financial infrastructure…part of the push for economic growth,” he outlined. Credit bureaus “have been a fundamental part of the whole improvement in how individuals and institutions now manage their risk in an integrated way. Whereas in the past, institutions would have to take the information that is given to them either by the client and other sources that they have to use intelligence to gather, now they can get it instantly, automated and at the click of a button, they can have the information of a customer sitting infront of them. It makes the application process more efficient and faster. It allows institutions to know how and who they can market their products to and what type of products they can market to individuals. It allows them to determine the credit terms that they will offer based on the credit history associated with the individual,” he added. He indicated that this has seen Jamaicans being more responsible because the list of institutions which credit bureaus collect information from to create a credit profile on an individual is extensive.
Article was originally published on the Jamaica Observer
Edwin Urasa appointed new CEO of Creditinfo Tanzania

New CEO Creditinfo Tanzania
Press Release
London, UK.
30/11/2021
Creditinfo Group is pleased to announce the appointment of Mr. Edwin Urasa as new CEO and Executive Director of Creditinfo Tanzania effective 01st November 2021. He is replacing Mr. Van Reynders whose tenure ended in April 2021.
Edwin brings 10 years of experience from the local banking industry having spent significant time around credit and risk management, recently before joining he was responsible for the Retail and Micro-SME segment at NBC Bank as Head of Retail Credit.
“I am especially excited to join Creditinfo Tanzania, which has been in operation for the last 9 years and has over the years continued to grow rapidly enabling small to large organizations effectively manage risk and support the government and banking community providing responsible lending in Tanzania. I am looking forward to expanding the companies’ product portfolio and services through application of best practices while leveraging Creditinfo global knowledge and expertise”.
“We are very excited to have Edwin Urasa join us as the new Creditinfo Tanzania CEO. With his vast knowledge and experience in the Tanzanian banking and credit industry, we have no doubt that he will lead Creditinfo Tanzania to greater heights and move the company’s journey forward in pushing our innovative solutions to the Tanzania market as well as pushing one of our core pillars – financial literacy, to the public at large”, says Paul Randall, CEO of Creditinfo Group.
Edwin holds a Bachelor Degree in Commerce (Hons), Majoring in Finance from the University of Dar es Salaam, an MBA from Edinburgh Business School at Heriot-Watt University-UK and has also several certifications namely, a Mortgage advisor (CeMAP)-UK, Modules in Commercial Credit from Moody’s Analytics-USA, and Risk Management from City University -UK.
ENDS.
PR contacts:
Marketing Manager/ PR for East Africa
Phidi Mwatibo
Email: Phidi.mwatibo@creditinfo.com
Creditinfo Group, TASDEEQ, PACRA and APL partner with Pakistan Banks’ Association to facilitate wider access to housing finance

Consortium will develop a market-level application scorecard and income estimation model to boost financial inclusion in Pakistan
LONDON, UK, 21st October 2021 – Pakistan Banks’ Association (PBA) recently announced that it has entered into a strategic partnership with a consortium of leading financial services and technology businesses to improve access to finance for low-income segments of the population currently excluded from traditional housing finance.
The consortium, comprised of Creditinfo Group, a global credit information and fintech service provider; TASDEEQ, Pakistan’s first SBP Licensed Credit bureau, offering cutting-edge reports, statistical scores, and analytical tools for the financial industry for efficient credit risk and strategic decision making; Pakistan Credit Rating Agency (PACRA) and Analytics Pvt Ltd, a leading Artificial Intelligence, Business Analytics, Big Data Analytics and Data Sciences solutions provider, will work together to develop for PBA a market-level application scorecard and income estimation model aimed at streamlining risk assessments and enabling a wider pool of applicants to access financing for their housing needs.
The consortium brings together industry-leading credit risk analytics knowledge, alongside extensive experience in Pakistan and emerging markets globally. The development and deployment of the automated income estimation & credit assessment methodology will be overseen through the PBA platform.
This project is being managed by the PBA Technology Working Group, comprising CEOs and members of Bank Alfalah, HBL and Faysal Bank as well as the CEO of PBA and a senior official of State Bank of Pakistan. This is a novel and unique project, and the first of its kind in Pakistan, where a scorecard will be developed using an alternative source of data.
The scorecard project will support the Naya Pakistan Housing Programme (NPHP), a government-backed initiative providing low-cost, affordable housing to deserving individuals in Pakistan that is expected to be a catalyst to accelerated economic activity and increased job opportunities in the region following the negative impact of Covid-19.
Mr. Tawfiq Husain, CEO, PBA stated, “We are very excited with the transformational impact this project can have on our members’ consumer lending and credit initiation and risk management capabilities. Starting with Low Cost Housing Financing, we hope to be able to put this model to use for other products in consumer lending.”
Mr. Omar Khalid, COO TASDEEQ commented: “TASDEEQ, PACRA and Analytics together bring a diverse array of expertise to the project. This synergy coupled with Creditinfo’s comprehensive global experience will be vital in development of low-cost housing credit scoring and income estimation models for the existing as well as new-to-bank customers utilizing alternative data sources. We are excited to be working with PBA to provide the banks with tools for quick and accurate risk decision making and working towards a more financially inclusive Pakistan.”
Mr. Samuel White, Regional Director, Creditinfo, commented on the partnership: “Our unique global experience will be complemented by the consortium partners’ local market knowledge to develop a robust credit risk and affordability solution in Pakistan. The project will provide PBA members with the required tools to make accurate risk decisions on underserved segments of the population, which is fundamental to increasing access to housing finance. Creditinfo is excited to work with the PBA to support the expansion of financial inclusion in Pakistan and help drive economic activity in the region”.
-ENDS-
About Creditinfo
Established in 1997 and headquartered in London, UK, Creditinfo is a provider of credit information and risk management solutions worldwide. As one of the fastest growing companies in its field, Creditinfo facilitates access to finance, through intelligent information, software and analytics solutions.
With more than 30 credit bureaus running today, Creditinfo has the largest global presence in the field of credit risk management, with a significantly greater footprint than competitors. For decades it has provided business information, risk management and credit bureau solutions to some of the largest, lenders, governments and central banks globally – all with the aim of increasing financial inclusion and generating economic growth by allowing credit access for SMEs and individuals.
For more information, please visit www.creditinfo.com
About TADSDEEQ
TASDEEQ is Pakistan’s first SBP Licensed Credit bureau and a leading credit information services company that leverages data analytics, technology, and industry knowledge to enable financial and non-financial institutions achieve their strategic goals with minimizing their credit risk and help consumers secure their future.
For more information, please visit www.tasdeeq.com
About PACRA
PACRA is, transforming both the rating business and the industry in line with the best practices. Today PACRA has more than 450 opinions outstanding and covering 60+ sectors and sub-sectors of economy.
Since inception, PACRA has over 8,000 rating opinion a testament of PACRA’s expertise, exceptional command, market leadership, and the confidence reposed in its opinions. PACRA rates more than 40% of KSE-100 index companies and 25% of the private sector debt, translating into a rating opinion on every 4th Rupee of debt raised in Pakistan.
The same trust and confidence have also been reposed by foreign regulators in PACRA’s ability and expertise as a CRA. PACRA has entered into a Technical Collaboration Agreements for the formation and operations of CRAs in Bangladesh (National Credit Ratings) and Sri Lanka (Lanka Rating Agency).
For more information, please visit www.pacra.com
About APL
Analytics (branded as Tenx.ai in North America) is a leading Artificial Intelligence, Business Analytics, Big Data Analytics and Data Sciences solutions provider. Having customers in the United States, Middle East and Pakistan, the company has accomplished a proven track record of successfully delivering high impact and complex projects.
For more information, please visit www.analytics.com.pk
About PBA
Pakistan Banks’ Association is a private limited company incorporated under the Companies Act 1913, (now the Companies Act 2017). The principal activity of the Association is to promote, advance and protect rights, privileges and interests of member banks/ financial institutions. Currently, it has 44 members on all Pakistan basis.
For more information, please visit www.pakistanbanks.org.pk
Media Contacts:
Matt Silver
Babel PR for Creditinfo
T: +44 (0)207 199 3977
Analysis of the Lithuanian construction sector

Financial and performance indicators in the construction sector reveal positive rather than negative trends. The boom in real estate emerging in the time of the pandemic has remarkably boosted the sectoral activity (during the first 6 months of this year alone the volume of constructions works grew by almost one fifth) and positively reflected in performance indicators of most of the companies. Sectoral earnings have been rapidly growing both on the domestic and foreign markets. After discounting the impact of seasonality and working days abroad, the volume of construction works is an increase of 21.5% year-on-year. The number of construction companies have been mushrooming, accounting for an increase by a third during the second quarter of this year compared to the previous year.
Financial statements filed by construction companies show that the number of construction companies in Lithuania in 2021 has grown by additional 531 from 15,784 to 16,316 (an increase of 3.4%) year-on-year. A very similar pace of growth (4.1%) was observed in the average corporate earnings (from EUR 809,994 to EUR 842,872). In terms of the staffing level, though, it has decreased slightly from 102,072 to 101,833. Despite a favorable situation, managers of construction companies are very cautious about the growth in the number of staff due to higher labour and other construction costs. Due to a more pessimistic mood in the sector, during summer this indicator started to decrease.
Another important positive factor is the decreasing number of debts and their aggregate values. For instance, during pre-pandemic August 2019 the number of corporate debts in construction industry stood at 12,336, with their aggregate value of EUR 128.7 mln. At the same period in 2020 the number of corporate debts stood at 11,539 compared against a reduced value of debt of EUR 94.3 mln. Although at the end of last August the number of corporate debts in the construction industry grew once again to 12,055, the aggregate debt value accounts for EUR 96.6 mln.
Some positive trends may be seen in the solvency of the construction industry. For instance, a year ago 23% of companies in this sector belonged to the high or highest group of bankruptcy risk, whereas this year the number of such companies dropped to 20%. In terms of delayed payments, some improvement may be observed too: last year the number of companies within the group of high and highest risk of delayed payments accounted for 47%, compared against 37% this year.
A number of construction companies going bankrupt has been decreasing steadily. In 2017-2020 the number of bankruptcies dropped from 366 to 163, whereas the updated statistics for this year give a solid ground to expect a further similar decrease in the number of reported bankruptcies.
Despite the reported drop in earnings in 2020 from 10% to 4% in comparison to 2019, other performance indicators in the construction industry have improved. For instance, the corporate sales median increased by 16% (from EUR 143,155 to EUR 166,133), the quick ratio has grown from 1.86 to 1.95, while the profit margin before tax increased from 1.25 to 1.35. The equity ratio has improved from 43.83 to 46.23, the accounts payable turnover decreased from 134 days to 128 days, whereas the accounts receivable turnover shortened from 57 to 51 day. EBITDA grew from 9.1 to 12.3%.
Jekaterina Rojaka,
Head of Business Development and Strategy, Creditinfo Lithuania
Creditinfo launches SME blended scorecard in Kenya

Credit information leader launches pan-African SME initiative, ahead of global rollout
LONDON, UK, 21st July 2021 – Creditinfo Group, the leading global credit information and decision analytics provider, is today announcing the launch of a scorecard solution tailored for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Through its unique approach to data and algorithms, this scorecard will help financial institutions improve their credit assessment and facilitate financing to the SME market, which has typically been less able to access finance.
Creditinfo, recognizing the importance of SME risk assessment across the world is aiming to roll out a global solution to address this challenge. The company will first launch the SME scorecard in Kenya, ahead of a wider rollout across countries in Africa, and several other key economies across the globe.
The unique modeling approach Creditinfo have developed significantly reduces, and in some cases eliminates, the human effort needed to assess customers’ risk profile based on credit data. It is delivered in a software platform which unifies, streamlines, automates and centralizes the risk evaluation process. Creditinfo’s SME scorecard is considerably stronger at predicting business failure than existing traditional models.
Burak Kilicoglu, Director of Global Markets at Creditinfo, commented, “SMEs drive innovation and push digitalization forward for many people by providing services to underserved segments of the population and creating job opportunities. SME scorecards will accelerate access to finance for the benefit of whole economic ecosystem. At Creditinfo we have access to a wealth of credit bureau data as a starting point, and so are uniquely positioned to offer this solution in global markets.”
Kamau Kunyiha, CEO of Creditinfo CRB Kenya, added, “Kenya is the most dynamic and receptive market for SME lending innovation, demonstrated by the successful adoption of mobile wallets and microloans. We look forward to seeing the economic impact of this new solution as it comes into full effect and we see more capital flowing through the SME economy.”
-ENDS-
About Creditinfo
Established in 1997 and headquartered in Reykjavík, Iceland, Creditinfo is a provider of credit information and risk management solutions worldwide. As one of the fastest-growing companies in its field, Creditinfo facilitates access to finance, through intelligent information, software and decision analytics solutions.
With more than 30 credit bureaus running today, Creditinfo has the most considerable global presence in this field of credit risk management, with a significantly greater footprint than competitors. For decades it has provided business information, risk management and credit bureau solutions to some of the largest, lenders, governments and central banks globally to increase financial inclusion and generate economic growth by allowing credit access for SMEs and individuals.
For more information, please visit www.creditinfo.com
PR contacts:
Marketing Manager/ PR for East Africa
Phidi Mwatibo
Email: Phidi.mwatibo@creditinfo.com
Increased use of credit bureau data in Lithuania

The use of credit bureau data is growing along with economic activity, although businesses tend to undertake additional precautions
The INTRUM EPR 2021 survey published in June reported on the growing demand for pre-payments against a decreasing trend of conventional risk management measures, such as credit history screening, insurance and factoring.
The current situation in the business sector could benefit from some clarifications and comments. In turbulent and uncertain times – and lockdown could rightly be said as being one of these – entrepreneurs tend to undertake additional safeguards, e.g. pre-payments. However, any quantitative easing measures, such as material support offered in the form of soft credits or subsidies, enabled many businesses to maintain their liquidity at least for some time. This is why the corporate performance results were not as devastating as they were during the Great Recession, when manufacturers importing commodities were forced to allocate all of their funds for pre-payments to their suppliers.
Meanwhile, the statistics demonstrates some late payments to the partners in 2021 in the sector of hospitality industry (by 9 days, from 41 to 50), in transport (from 56 to 62 days), in services (from 38 to 41 days), in processing industry (from 38 to 40 days). In contrast, in the financial operations sector, the payment terms have become shorter.
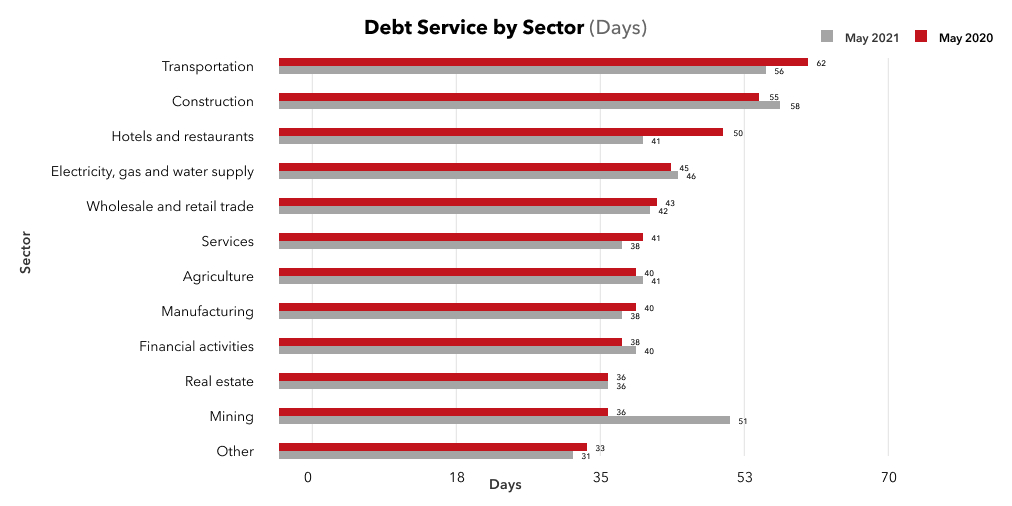
Quite reasonably, one may wonder what are the reasons behind shorter payment terms – can these be explained by precautions taken by the suppliers or by an improving economic situation?
I would like to draw the attention to the fact that in the times of the pandemic shareholders would recommend public sector representatives tightening payment gaps to enable the business sector to improve liquidity in the private sector. In the private sector the medium-term payment gaps were affected by a more resilient economic structure, as businesses suffering from liquidity shortage made only a fraction of all businesses.
Moreover, account needs to be taken of the fact that as many as 60 percent of companies responding to the INTRUM survey in Lithuania admitted anticipating recession in contrast to economic forecasts showing a clear recovery.
Lithuanian business market is rather optimistic: the economic evaluation index in Lithuania has already reached its pre-pandemic level (116 vs. 110), this indicator was higher only in 2007 on the eve of the Great Recession. In addition, all sectors last May demonstrated a growing confidence index. Commercial confidence index grew by 9 percentage points, while in the service, industry, and construction sectors it grew by 7, 4, and 1 percentage points, respectively. Only the consumer confidence index dropped by 3 percentage points.
In parallel, a rapid growth in the real estate prices and demand is being reported along with the signs of growth in the prices of commodities and inflation. All these factors may signal the approaching peak in an economic cycle, which explains the lingering anxiety about a possible recession due to the phasing-out of economic stimulus measures.
One of the most popular support measures – tax deferrals – are drawing to an end: default interests and tax recovery procedures will not be calculated until 31 August 2021 and for two subsequent months; one may expect to see a more realistic state of business health towards the end of the year.
Nevertheless, the following conclusion has to be drawn as a comment on the use of credit office information systems by the organizations: the number of inquiries recently has been changing along with the economic activity – within the first 5 months the number of inquiries increased by 12 percent compared to 2020 year-on-year, and by as many as 25 percent compared to 2019 year-on-year.
Jekaterina Rojaka,
Head of Business Development and Strategy,
Creditinfo Lithuania.
Creditinfo Lithuania study: Men earn more than Women

In Lithuania men earn more than women in 72 economic sectors, while women do so in 9 sectors. Human resource specialists recommend inquiring more boldly about corporate career and pay policies.
The study conducted by Creditinfo Lithuania suggests that out of 81 sectors into which economic activities of Lithuania-based companies are broken down, in 72 of them men earn more than women on average. Pay for men usually exceeds pay for women by roughly 30-50 percent, while the largest positive gender gap of 19.2 percent in favor of women has been recorded in education. In the reminder eight sectors women usually earn 8.5 percent more compared to men on average. The most striking gender pay gap favoring men is reported in 30 economic sectors where the highest monthly pay may range from EUR 1,464 to 2,671. Human resource specialists recommend staff inquiring about corporate pay and career policies.
As of May, when Sodra started publishing gender pay gap data, the credit bureau Creditinfo Lithuania has analyzed pay received in various economic sectors. The study suggests that in an absolute majority of activities, especially those with the highest pay, men usually earn more than women on average: in telecommunications (50.1 percent), in medicinal products and pharmaceutical services (47.8 percent), in veterinary activities (45.1 percent), in insurance and reinsurance (41.9 percent), in financial services (43.3 percent), in cinema and TV programme production (40,4 percent), in manufacturing of power generation equipment (38 percent), operation of headquarters and consultation activities (35.6 percent), in information services (37 percent), in production of computer, electronic and optical devices (34.8 percent), in research and experimental activities (34.8 percent), in programme production and broadcasting (34 percent).
Sectors which particularly stand out are air transport, gambling, and gaming industry, where men earn 95.1 to 127.6 percent more than women on average.
There are several sectors where women are usually higher earners, such as: education (19.2 percent), land transport and transportation by pipelines (10.7 percent), social work (11.6 percent), in-house social care activities (8.3 percent), furniture production (7.2 percent), postal and courier services (6.2 percent), manufacturing of tobacco products (5.8 percent), and manufacturing of metal products (5.1 percent).
Publication of gender pay gap will boost corporate sustainability
According to Jekaterina Rojaka, the head of corporate strategy and development at credit bureau Creditinfo Lithuania, while analyzing the corporate operations other factors, in additional to the financial indicators, such as earnings and profit, are becoming increasingly more relevant – these factors determining the overall corporate reputation include operational transparency, corporate values and internal culture, staff and social responsibility policies.
“Sustainability is starting to play a more important role on the corporate creditworthiness and reliability, as it entails transparency in corporate policy on staff relationship, corporate policy on partners and communities, and contribution to solutions of issues important for the society”, J. Rojaka says. Statistics on average pay by men and women supplements information about the prevailing motivational instruments used by the company and career opportunities.”
According to J. Rojaka, gender pay gap is a particularly sensitive issue also because on the Lithuanian labour market men and women enjoy an equal employment rate. The Eurostat data suggests that in the age group of 20-64 in Lithuania the gender employment rate gap (with 79 percent of men and 77.4 percent of women having employment) is the lowest in the whole of the European Union, accounting for a mere 1.6 percent in Lithuania.
According to the data of the Department of Statistics of Lithuania, in 2020 in Lithuania there were 1.358 mln. people having employment – 679.9 thousand and 678.2 thousand of men and women, respectively. The employment rates of men and women in different economic sectors varies. For instance, there are many more men than women engaged in agriculture (2.06 times more or 52.2 thousand versus 25.1 thousand, respectively), in power and gas supply (4.3 times more, or 7.7 thousand and 1.8 thousand, respectively), in water supply and wastewater treatment (2.5 times more, or 13.1 thousand and 5.2 thousand, respectively), in construction (10.7 times more, or 91.2 thousand and 8.5 thousand, respectively), in real estate operations (1.6 times more, or 7.7 thousand and 4.8 thousand, respectively).
There are sectors, though, where women’s employment rate is several times higher than that of men’s, these sectors are: health care and social work (6.1 times higher, or 13.6 thousand and 83.1 thousand, respectively), education (3.9 times higher, or 27.7 thousand and 106.9 thousand, respectively), accommodation and catering (2.4 times higher, or 9.9 thousand of men compared to 23.7 thousand of women).
Among the sectors with a similar level of employment rate among both genders the average salaries paid to men remain higher than salaries of women. These sectors include wholesale and retail (104.1 thousand of men and 114.8 thousand of women), information and communication (23.6 thousand and 15.6 thousand), financial and insurance activities (9.9 thousand and 16 thousand), administration (30.8 thousand and 26.2 thousand), public administration and defense (43.2 thousand and 43.2 thousand), creative and leisure activities (10.1 thousand and 16.6 thousand).
Meanwhile, the representative of Creditinfo notes that while analyzing average salaries paid in any individual company account shall be taken of the gender balance, the positions held by men and women, as well as the competences and experience needed in the given position. Moreover, she notes that, for instance, in air transport pilots are usually men, while women mainly work as flight attendants, which explains a huge gender pay gap in the air transport sector.
Human resource specialists recommend analyzing data carefully and discuss about career and pay more boldly
Šarūnas Dyburis, the Managing Partner at AIMS International Lithuania, notes on a shrinking gender pay gap among staff with the same level of competences and experience.
“Overall, within the European Union Lithuania is somewhere in the middle in terms of gender pay gap – an average pay for men is 13.3 percent higher than that for women, compared against an EU average of 14.1 percent”, Š. Dyburis said. Our country stands out in that the gender pay gap has dropped to the minimum among men and women with the same level of experience and competences. However, due to objective reasons, such as career breaks due to maternity leave, women reach the highest pay levels slightly later than men, which also affects the average salaries”.
The head of AIMS International Lithuania notes on an increasing popularity of corporate motivational and pay policies in Lithuania offering clearer career possibilities, encouraging the pursuit of higher performance indicators, and strengthening of cooperation spirit within organizations.
“We would like to encourage women plan their career path more boldly, be more proactive in seeking new career opportunities, and negotiating for higher pay more ambitiously. All candidates without exception should openly inquire about corporate career policies and learn about staff achievement appraisal and motivational systems”, recommended Š. Dyburis.
For more information see:
- https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Gender_statistics#Labour_market
- https://osp.stat.gov.lt/lt/statistiniu-rodikliu-analize?hash=f3f0ba78-6fb2-433f-ad92-ef032be74a9e
For more information contact:
Jekaterina Rojaka, Head of business development and strategy at Creditinfo Lithuania (jekaterina.rojaka@creditinfo.lt; +370 612 73515)
Šarūnas Dyburis, the Managing Partner at AIMS International Lithuania (sarunas.dyburis@aims.lt; +370 616 72727)
How to build an impeccable credit history

Within the first days of our lives, we are all issued a birth certificate which becomes the first document of the pile that we are to collect during our lifetime. Birth certificates are followed by passports, then graduation certificates, college or university diplomas. Reaching the age of majority entails, among other things, responsibility not only for one‘s professional career, but also for financial decisions which are reflected in the credit history. In other words, credit history is a yearbook of one‘s financial obligations, which is read by banks, leasing companies or other institutions in order to assign you to the categories of either reliable or less reliable clients and decide whether they are willing to accept you for credit.
No Credit Without Credit History
According to the surveys, more than half of the adult population of Lithuania are active users of credits to finance purchase of the real estate, vehicles, household appliances, furniture, PCs, phones, etc.
To get a credit, you apply to the banks or leasing companies. They first look into your credit history which shows how well you performed our financial obligations in the past, including consistency of timely payments for electricity, telecommunication services or garbage removal, also timely repayment of other credits and any overdue debts.
A good or bad credit history determines whether you will be accepted for credit to buy a new refrigerator instead of an old broken one, whether sellers will agree to sell you a new phone just after signing an agreement on payment in installments over the next two years. If the credit history is sound, you can expect the most favorable conditions and trust of the seller. A poor credit record means that you may have to pay the entire amount at once.
A History of Amounts and Discipline
The credit history reflects two types of information. The first one is an account of financial obligations, credits in the banks, consumer loans from credit institutions or peer-to-peer lending platforms, leasing, etc. Lenders use this information to assess the client‘s budget sufficiency, i.e., the percentage of income spent for servicing the existing debts. The second type of information is the track record of repayment of debts indicating the discipline of making payments for credits, mobile phone, internet, cable TV and other bills.
Banks Favor Positive Rather than Empty Credit History
The staff of the credit bureau is often asked what a good credit history is. One may think that lenders favor those who never had a loan, leasing or credit card, and never delayed payments to service providers, hence their credit history is empty. Yet the lenders‘ approach is different. On the one hand, an empty credit record may indicate that you had no need to borrow or to buy on lease in the past. On the other hand, who is more trustworthy: a client who repaid his lease or loan in time, or a person who never had any financial obligations? A survey conducted by “Mano Creditinfo“ revealed that banks tend to be more favorable towards clients who had financial obligations in the past as they are more predictable.
Financial institutions tend to trust clients with good credit history and offer them better conditions, such as a lower down payment, lower interest rate and more flexible repayment terms. For instance, Swedbank‘s Institute of Finances earlier advertised that good credit history may save up to several thousand euros in interest on home loans. Good credit history will save you up to EUR 500 on a loan for a EUR 5,000 worth car, or up to EUR 1,700 on a EUR 10,000 worth car lease.
Can You Fix a Bad Credit History?
Yes, you can, but it will take time and effort. There are several factors that determine a bad credit history, including high financial obligations, excessive and unreasonable borrowing, borrowing to service outstanding debts, delayed payments and other. If your credit history contains any such events, you have to brace yourself for a hard time, as cosmetic adjustments will not erase or eliminate them. If you tend to assume too many financial obligations, you will have to reduce their number and curb your appetite for borrowing for some time at least. If you have any overdue payments, you are recommended to make the payments as soon as possible and never delay them again.
Financial institutions usually analyze the credit history of the recent 2 or 3 years, and the negative impact of the sins of the past gradually fades away over time. Thus, if you have a poor credit history and decide to change your approach towards your financial obligations today, financial institutions may still have questions about your past financial behaviour for a couple more years to come.
Mistakes to be Avoided
Information about the financial relations and obligations will accompany you throughout your entire life telling a story of either a high financial discipline or lack of it. If you decide to borrow, you must carefully assess your ability to cover the debt and think about the ways to ensure the repayment even if you lose your income. Negative records appear in your credit history very quickly, within a month from the day the payment was due. Erasing this record from your credit history will take years, though.
Aurimas Kačinskas,
CEO – Creditinfo Lietuva.




